
SOL
Solana
crypto
staking
Solana Insights & Analysis: 2024 Annual Report | Everstake
Explore Solana staking trends and performance in the 2024 report. Key insights on developments, metrics, rewards, and the evolving Solana ecosystem
JAN 29, 2025
Table of Contents
Key Insights and Takeaways
Methodology
Main Releases, Partnerships, Ecosystem Milestones
Key Network Metrics Analysis
State of Decentralization
Solana Network Performance
Solana Restaking
Future Prospects
Share with your network
In 2024, Solana further reinforced its position as one of the leading blockchains thanks to advancements like stake-weighted QoS, token extensions, Solana Actions & blinks (blockchain links), Frankendancer, and more. The Solana ecosystem has also expanded with the integration of more DeFi, NFT, and Web3 projects and focusing on interoperability with other blockchains through bridges and protocol updates. Additionally, the platform has invested in better developer tools, documentation, and grants, encouraging new decentralized applications and further establishing Solana as a competitive, high-performance blockchain.
This report analyzes data from December 2023 to December 2024.
Key Insights and Takeaways
-
In October 2024, Solana reached 120 million daily active addresses within the network.
-
As of December 2024, Solana achieved an all-time high (ATH) of approximately 138 million daily transactions, showcasing its scalability and growing adoption across dApps and services.
-
Total Value Locked (TVL) on Solana rose to $9.5 billion in December, marking its highest level since January 6, 2022.
-
The network hosts over 5,170 nodes across 46 countries and 204 cities, with approximately 1,400 mainnet validators distributed across 282 data centers globally.
-
In H1 2024, prominent validators Galaxy and Helius entered the top 5 Solana validators by total stake, joining Binance, Coinbase 02 and Ledger by Figment.
-
Solana maintained exceptional reliability, with 100% uptime and no incidents for nearly a year. The only outage occurred in February 2024, resulting in a network downtime of about five hours.
-
Everstake still stands out as the leading validator in Solana, with over 166,000 stake accounts entrusting their SOL tokens to the platform.
-
In 2024, restaking in Solana gained noticeable steam. This functionality enables token holders to re-stake their assets across multiple protocols, enhancing the network’s security, scalability, and decentralization.
Methodology
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Solana blockchain, using the data practices and sources described below to ensure a comprehensive and reproducible study.
On-chain Data Collection
We collected extensive data directly from the Solana blockchain. This included raw transaction data, information on staking, inflation metrics, and other relevant data points.
Data was gathered through Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) to public nodes on the Solana network. These RPC calls facilitated the retrieval of real-time and historical blockchain data. To ensure data reliability and availability, we stored the gathered data in relational databases (DBs), allowing for efficient querying and analysis.
Data Preparation
The collected data was meticulously cleaned and formatted using Python. To ensure the dataset's integrity, we manually handled missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
The data was merged from various sources, ensuring a cohesive dataset for analysis. This includes integrating data from the blockchain with API-sourced information on staking, transactions, and inflation. The initial data visualization and exploratory analysis used PowerBI, which was substantial in identifying key trends and patterns.
Data Analysis
We conducted a comprehensive analysis of the prepared data, employing a range of statistical methods and analytical techniques. This included generating graphs, charts, and visualizations to illustrate key metrics such as staking trends, transaction volumes, and inflation rates.
Identifying significant trends and correlations within the data used hypothesis testing.
Interpretation
Our research and development team interpreted the findings from the data analysis. We additionally compared our findings with existing research and industry benchmarks to obtain insights into the Solana blockchain's performance and trends.
Based on our findings, we formulated recommendations for future research and potential actions to optimize blockchain performance and usage. By detailing our methodology, we aim to provide transparency and enable reproducibility of our study, allowing others to validate and build upon our work.
Main Releases, Partnerships, Ecosystem Milestones
In 2024, several important announcements and ecosystem expansions related to Solana contributed greatly to the blockchain’s position and reputation as one of the most innovative in the ecosystem.
Token Extensions
Token extensions are an evolution of the Solana Program Library (SPL) Token standard, offering enhanced capabilities that go beyond the basic functionalities of the original Token program. While the initial SPL Token standard enabled core features like minting, transferring, and freezing tokens, the Token Extensions framework introduced advanced functionality to meet modern blockchain needs.
Some of the Token Extensions include:
-
Confidential Transfers: Safeguards the confidentiality of user balances during transfers while concealing transaction amounts.
-
Transfer Hooks: Grants token issuers control over which wallets can interact with their token and defines how tokens and users engage with each other.
-
Transfer Fees: The capability to implement fees directly at the protocol level.
Additionally, it empowers developers to create more versatile tokens tailored to complex use cases such as decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, and institutional-grade assets.
Stake-Weighted QoS
Core developers introduced Stake-weighted Quality of Service (QoS) as a new feature for Solana validators. This mechanism prioritizes network traffic based on the amount of stake held by a validator, ensuring those with higher stakes receive enhanced connectivity. This improvement allows validators with substantial stakes to process and transmit transactions more efficiently.
Enabling Stake-weighted QoS requires validator nodes to be paired with highly trusted RPC nodes, which is particularly beneficial when both functions are managed within the same infrastructure. The feature operates in a trusted environment, where the validator and RPC nodes must reach a prior agreement before activating Stake-weighted QoS.
Actions & Blinks
Solana Actions are specification-compliant APIs designed to streamline blockchain interactions. They enable users to preview, sign, and send transactions on the Solana blockchain without leaving their current environment. These actions can be integrated into various contexts, such as QR codes, buttons, widgets, and websites.
A key feature of Solana Actions is blockchain links (or blinks), which turn any Solana Action into a shareable, metadata-rich URL. This allows Action-aware clients—such as browser extension wallets or bots—to display additional functionality for users. For instance, on a website, a blink can trigger a transaction preview in a wallet without needing to open a dApp. In platforms like Discord, a bot could expand the blink into an interactive set of buttons.
Essentially, the feature enables users to interact with the blockchain directly through any web surface displaying a URL, making on-chain interactions more accessible.
ZK Compression
ZK Compression is a technology that significantly reduces the size of data stored on the Solana blockchain, particularly for tokens and accounts. This is crucial because, on Solana, all interactions and data are stored in accounts, such as PDAs (Program Derived Addresses), which form the backbone of the network’s architecture. Each account contains important data, including token balances, transaction histories, and program configurations. That said, the large volumes of data generated by active applications can bring about higher storage costs.
By implementing ZK Compression, Solana developers can drastically reduce storage requirements without compromising the blockchain’s security or speed. This technology enhances scalability and lowers operational costs, making it easier for developers to build efficient, high-performance applications. Thus, Solana becomes better equipped to support large-scale, data-intensive applications while maintaining its core strengths of speed and low fees.
Frankendancer
The launch of Frankendancer, an early version of the Firedancer validator client that is set to radically improve Solana’s performance, marked an important step toward the latter's full mainnet release. Frankendancer employs a tile-based architecture, where each tile represents a thread linked to a specific CPU core, handling dedicated tasks in a continuous loop. This architecture enables efficient data flow and parallelism, which are essential for high performance.
The system consists of several tiles, each responsible for different components of transaction processing. These include a net tile for managing network interactions, a quick tile for protocol operations, signature verification tiles, a TPU tile for deduplication, a pack tile for transaction selection, bank tiles for execution, a POH tile for ordering, and a shred tile for block distribution.
Key Network Metrics Analysis
A closer look at Solana’s key metrics in 2024 suggests significant growth, a noticeable increase in adoption, and impressive performance.
Daily Active Addresses
Daily active addresses are a strong indicator of user engagement and ecosystem activity. In October 2024, Solana peaked at 120 million active addresses. The record in 2024 was set on October 22, with 9.4 million active addresses in a single day. Key contributors to this surge include platforms like Pump.fun, which generated over $30.5 million in revenue, and the decentralized exchange Raydium, which facilitated trades surpassing $30 billion during the month, according to DefiLlama.
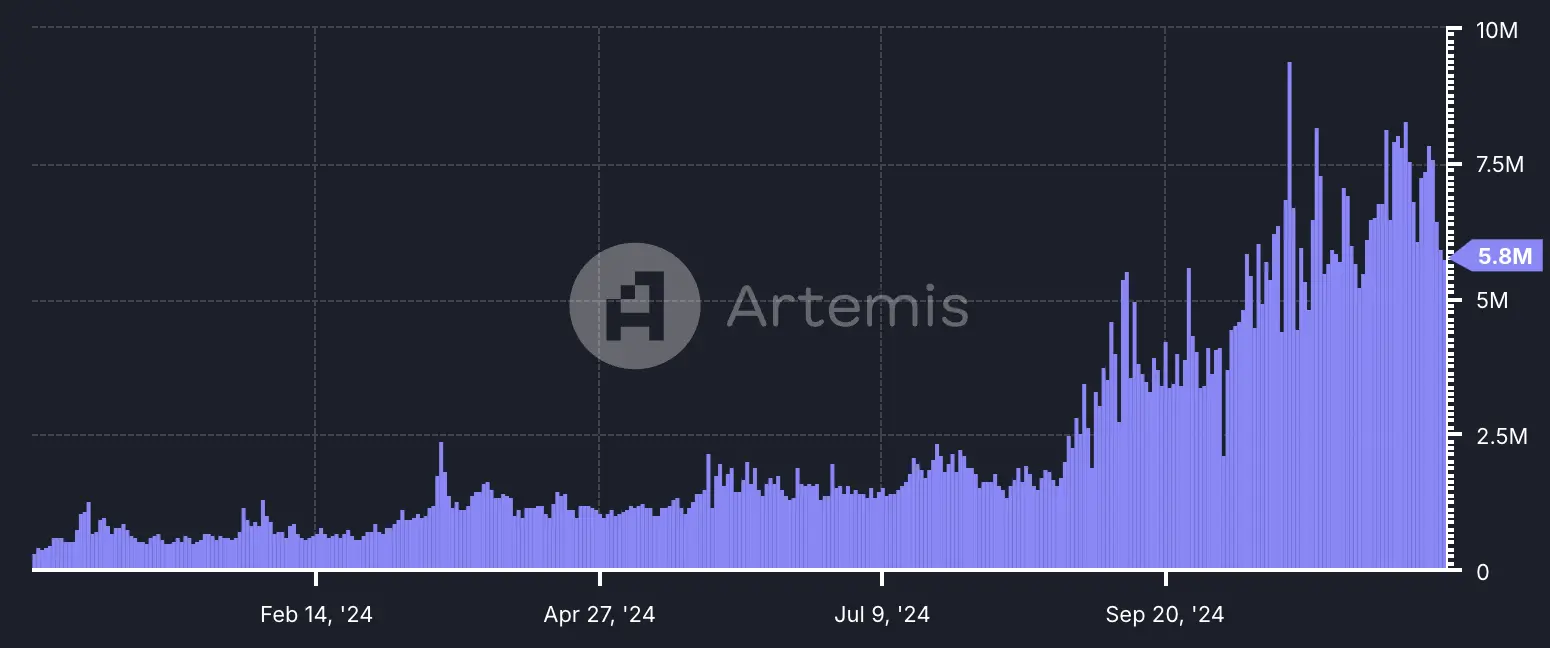
Source: Artemis
Transactions
At the end of December, the network achieved an all-time high (ATH) of approximately 138 million daily transactions (successful and reverted transactions). The network's efficiency and low transaction fees have attracted a diverse user base.
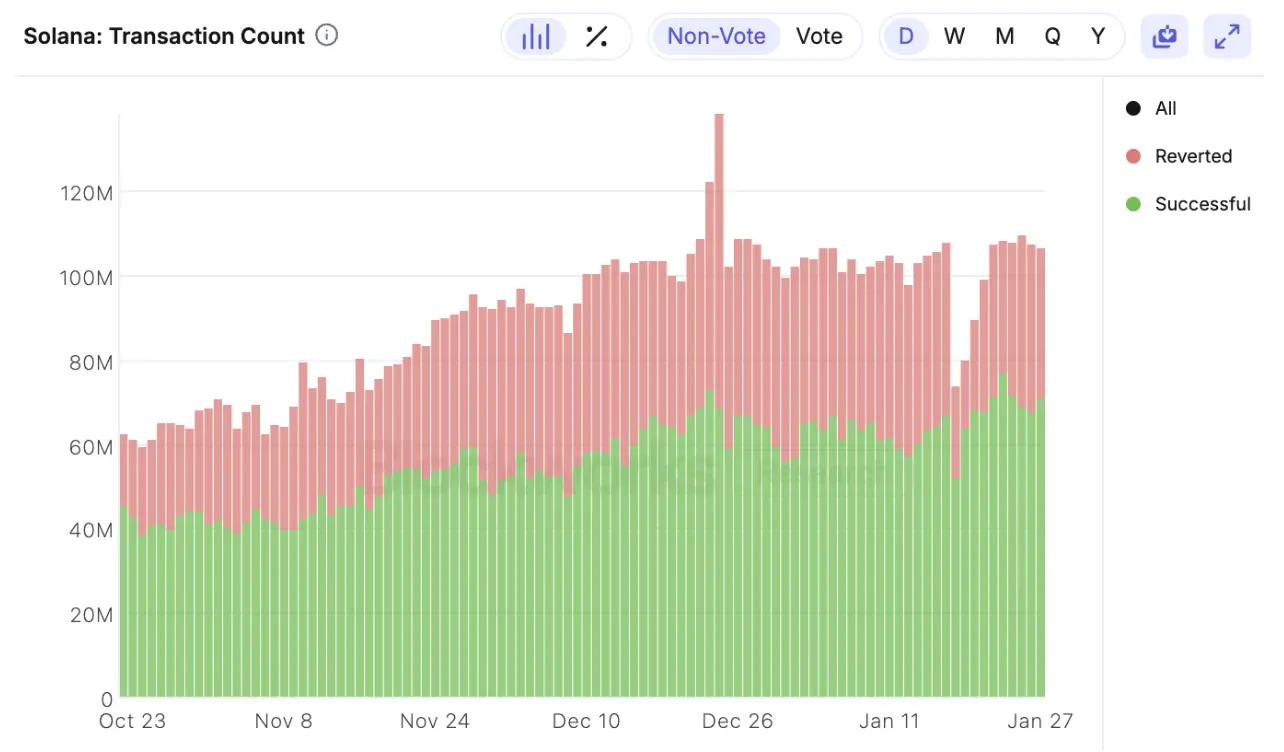
Source: BlockworksResearch
REV
Network REV (Real Economic Value) is a standardized metric used to track the value a blockchain accrues through user activity. It encompasses both in-protocol transaction fees and out-of-protocol tips paid by users for transaction execution.
The ATH for Solana's REV occurred on November 20, when it reached approximately $27.6 million. The ATH in REV stems from the Solana ecosystem’s ongoing scalability efforts and the dynamics of its fee structure, which continues to support high-throughput applications.Jito Labs delivered exceptional results on November 20, generating $14.3 million in tips alone, underscoring the increasing demand for MEV extraction services on Solana.
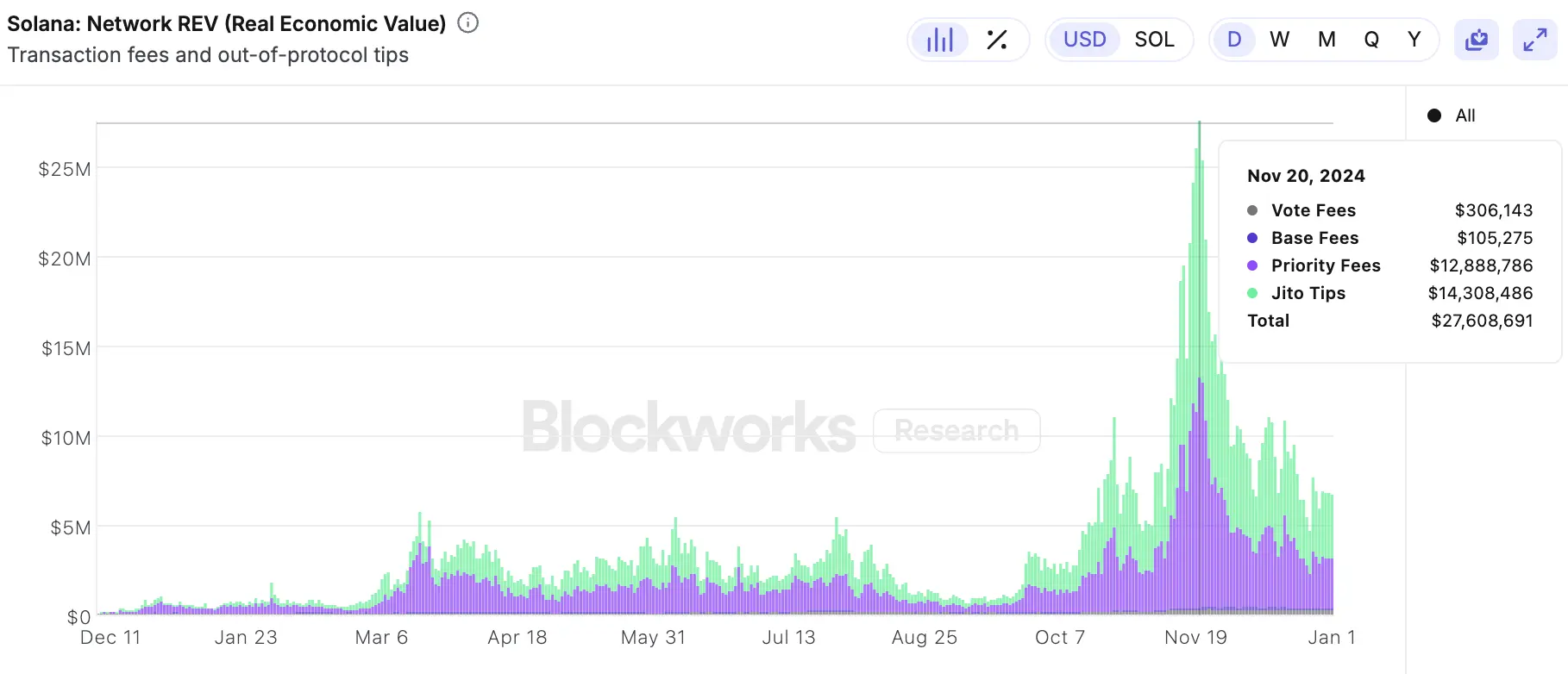
Source: BlockworksResearch
DEX volume
The decentralized exchange (DEX) ecosystem on Solana has experienced significant growth in 2024. Major DEX platforms built on Solana, such as Orca and Raydium, have seen increased trading volumes thanks to the network's high speed and low fees.
Solana's DEX ecosystem achieved record-breaking monthly trading volumes in December, surpassing $188 billion. This marked a remarkable increase of 8 times since the beginning of the year.
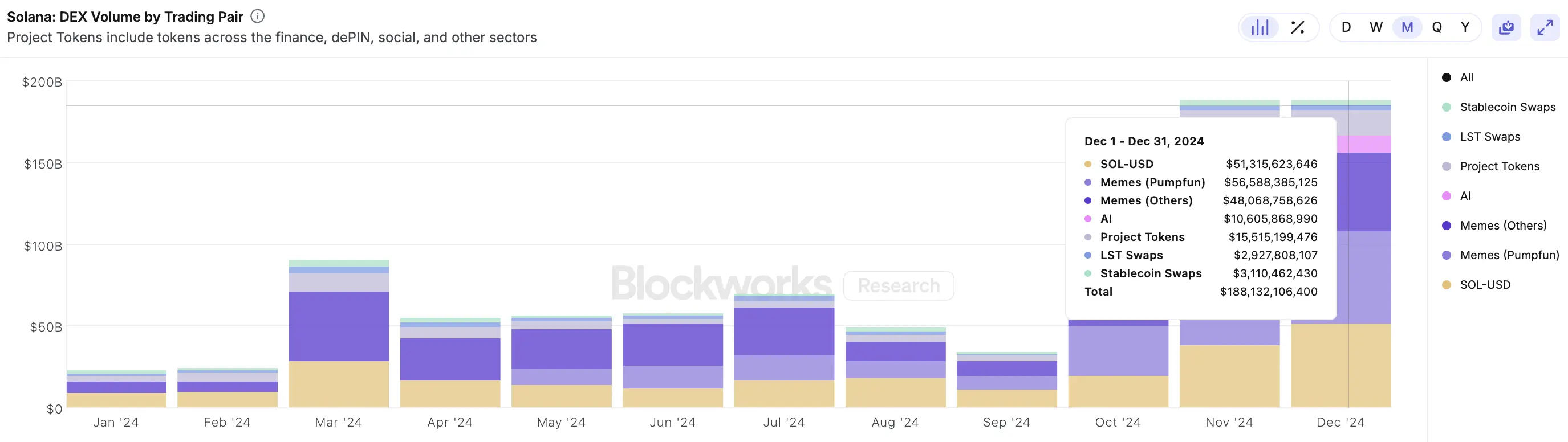
Source: BlockworksResearch
TVL
Total Value Locked (TVL) on Solana climbed to $9.5 billion in December, reaching its highest level since January 6, 2022.
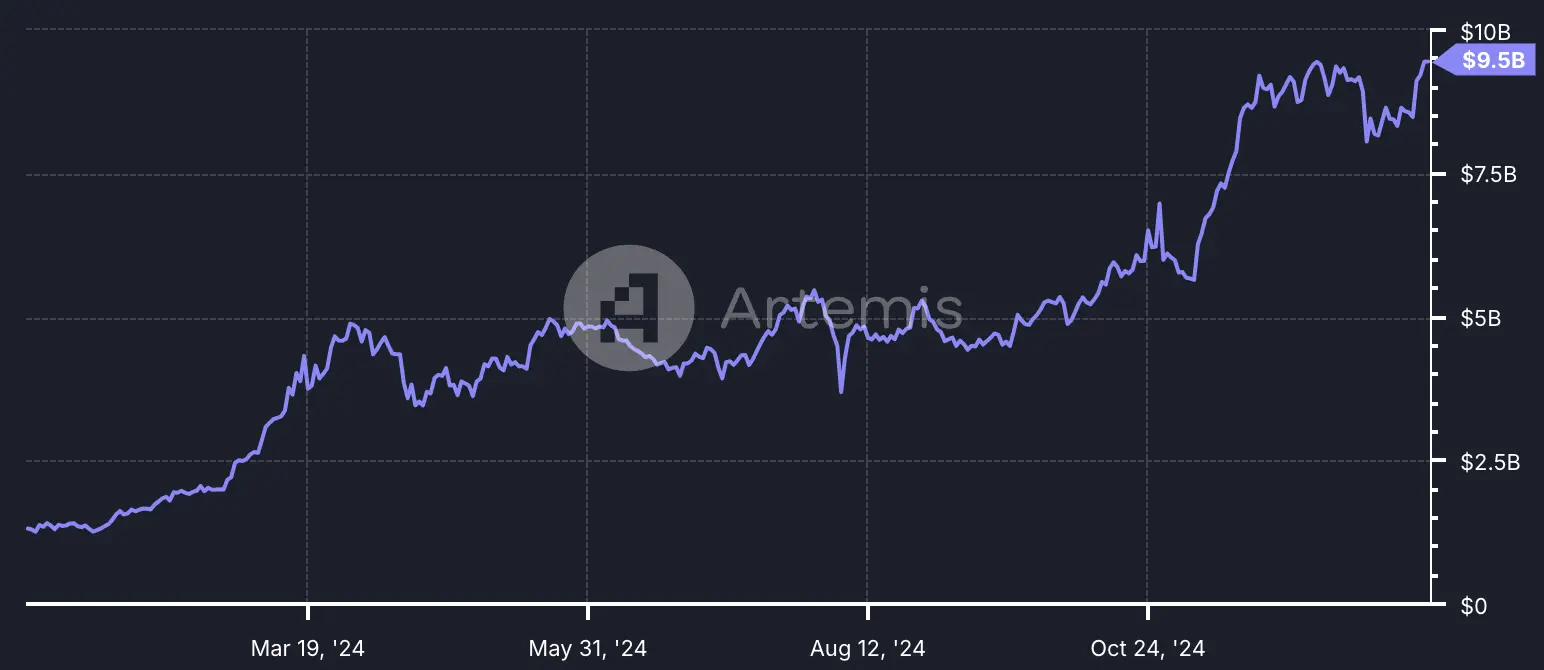
Source: Artemis
Overall, in Q4 2024, the Solana blockchain experienced substantial growth, driven by a combination of positive market sentiment and substantial ecosystem expansion. As it attracts more developers, projects, and institutional players, the ecosystem keeps establishing itself as a key player in technological innovation in finance and community building.
State of Decentralization
In 2024, Solana remained one of the most decentralized blockchains.
Nakamoto Coefficient
The Nakamoto coefficient is a metric used to evaluate the decentralization and security of a blockchain network. It measures the network's resistance to potential takeovers by malicious actors or groups as the minimum number of nodes that must collude to gain control of more than 33.33% of the network's stake. A higher coefficient signifies greater decentralization and security, reflecting a broader distribution of mining or staking power among participants.
At the time of writing, Solana’s Nakamoto coefficient stands at 18, reflecting a high degree of decentralization within the network. This metric exceeds that of several other prominent networks, such as Polygon (4), Cosmos (7), MultiversX (7), and Celestia (7).The Nakamoto coefficient is currently considered competitive within the industry. Still, its actual value might be lower since various entities can manage multiple validators under the radar. According to the publicly available data, no individual validator holds more than 3.2% of the total stake.
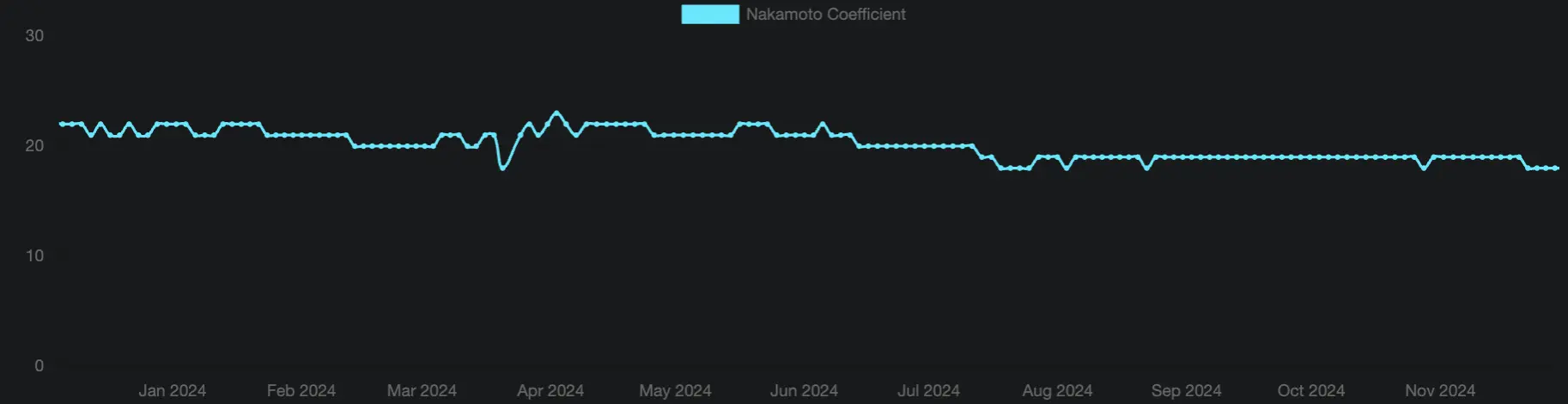
Source: Solana Compass
Number of Validators and Node Distribution
As of late 2024, there are over 5,170 Solana nodes distributed across 46 countries and 204 cities worldwide. Approximately 1,400 of these are mainnet validators spread across 282 data centers globally. The geographic distribution enhances network resilience and decentralization. The map below shows the geographic distribution of all nodes, while the accompanying bar charts provide detailed insights into their allocation by country and city.
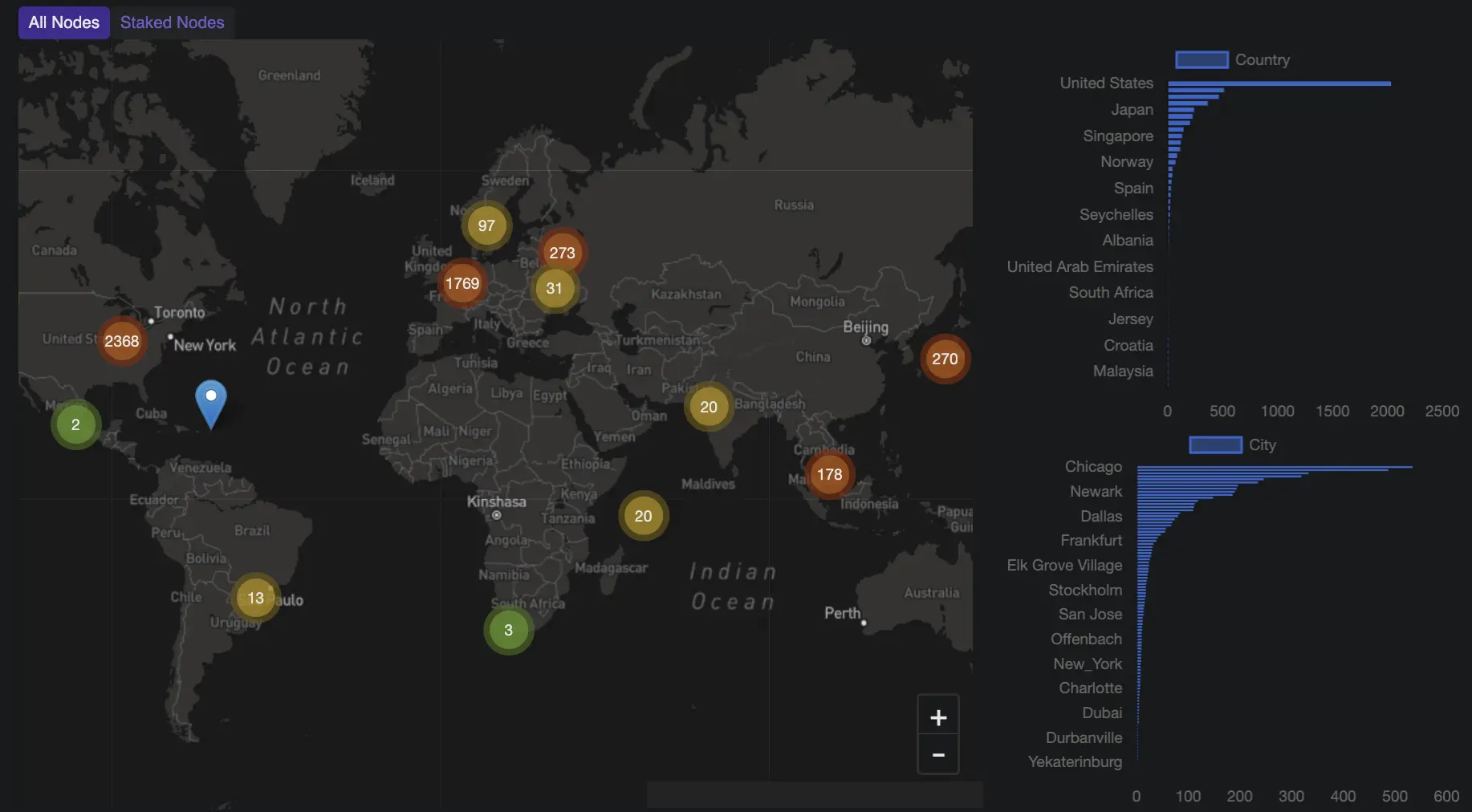
Source: Solana Compass
The majority of validators and the stake are located in Europe (46% of validators, with 68% of stake), followed by North America (40% of validators and 20% of stake). The largest concentrations are in the United States, the Netherlands, and Germany.
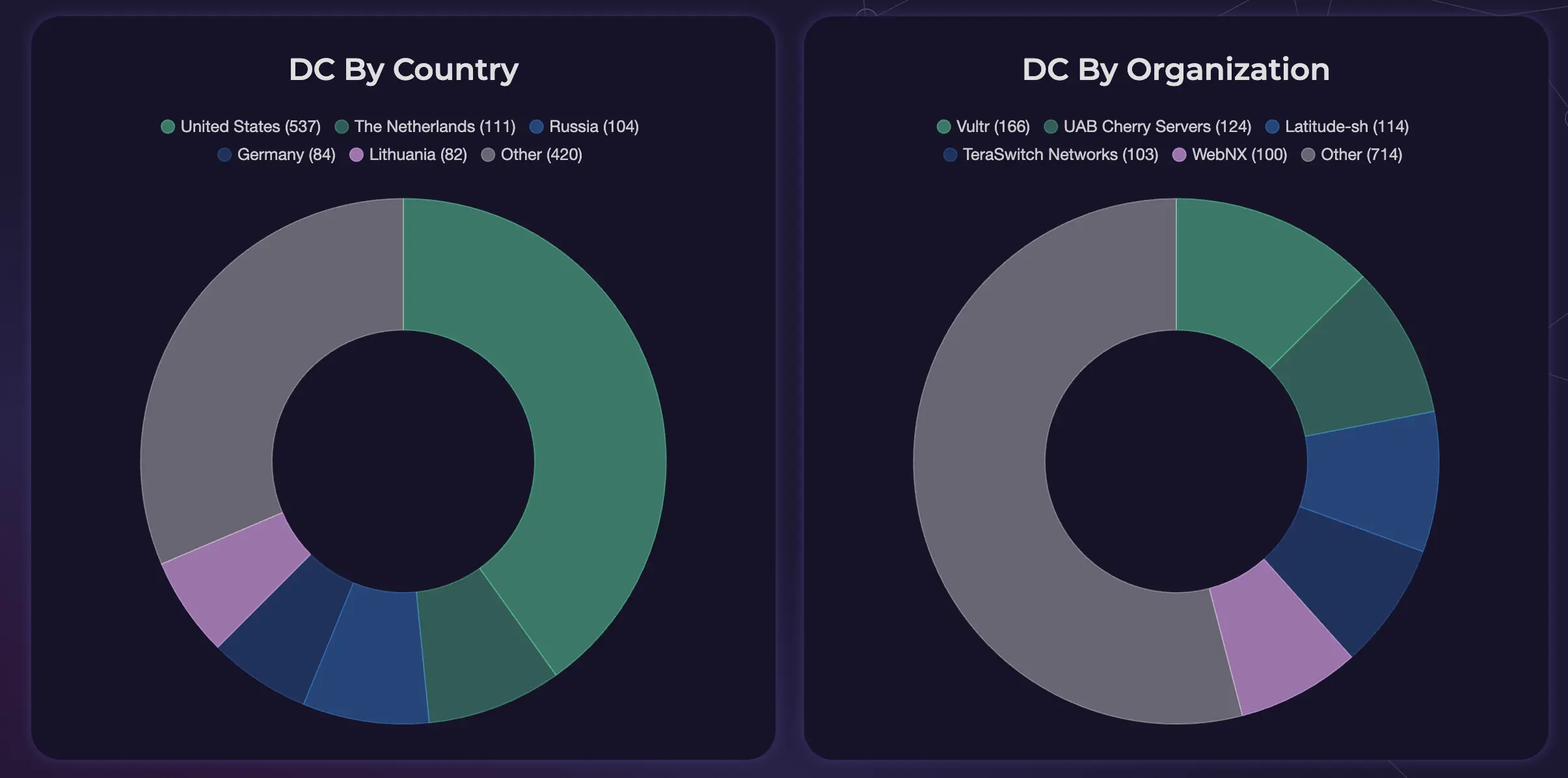
Source: Validators.app
Validator Clients
Validators are machines running a Solana validator client, forming the backbone of the network's operations. Diversifying software clients is essential for strengthening the resilience and decentralization of any blockchain, as it reduces the risk of a single point of failure in the infrastructure. Solana's recent transition to a multi-client ecosystem represents a significant stepping stone as it provides validators with the freedom and flexibility to choose from multiple clients.
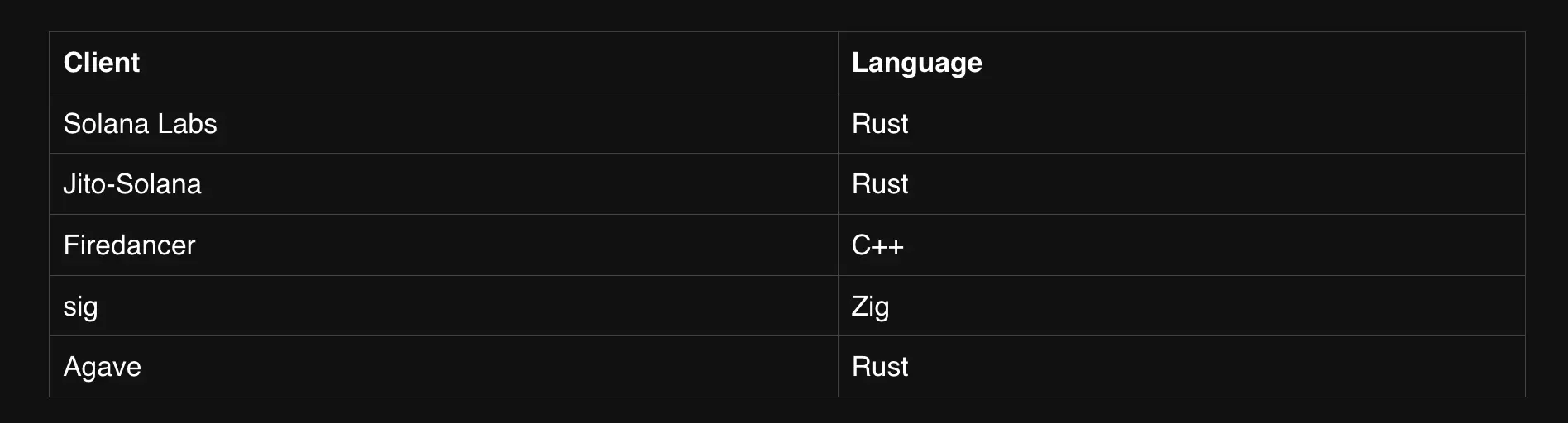
Source: Solana.com
-
Agave is a validator client maintained by the Anza core engineering team. It is a fork of the original Solana validator software.
-
Jito is the first third-party, MEV-optimized validator client for the Solana blockchain. Released by Jito Labs in August 2022, it is based on Solana Labs' code but is developed and maintained independently.
-
Firedancer is an independently built validator client by Jump Crypto. It is designed to improve and complement the capabilities of the original Solana validator client.
-
Frankendancer is a hybrid validator implementation combining the elements of Firedancer and Agave code running in parallel. It replaces Agave's networking stack and block production components to deliver enhanced performance in leader roles. As a full Firedancer validator is still under development, Frankendancer serves as a transitional solution.
-
Sig is a highly optimized Solana validator implementation developed using Zig, a modern low-level programming language focused on performance and efficiency.
Stake Distribution
The stake distribution within the Solana network shows a high degree of decentralization.
Galaxy and Helius entered Solana's top ranks in the first half of 2024. Helius began operating its validator in April 2024, adopting a competitive approach by offering 0% commission fees and 0% MEV fees. This strategy has proven effective, as Helius has since attracted over 16,000 delegators with an aggregated stake of 12 million SOL. The chart below illustrates the distribution in superminority.
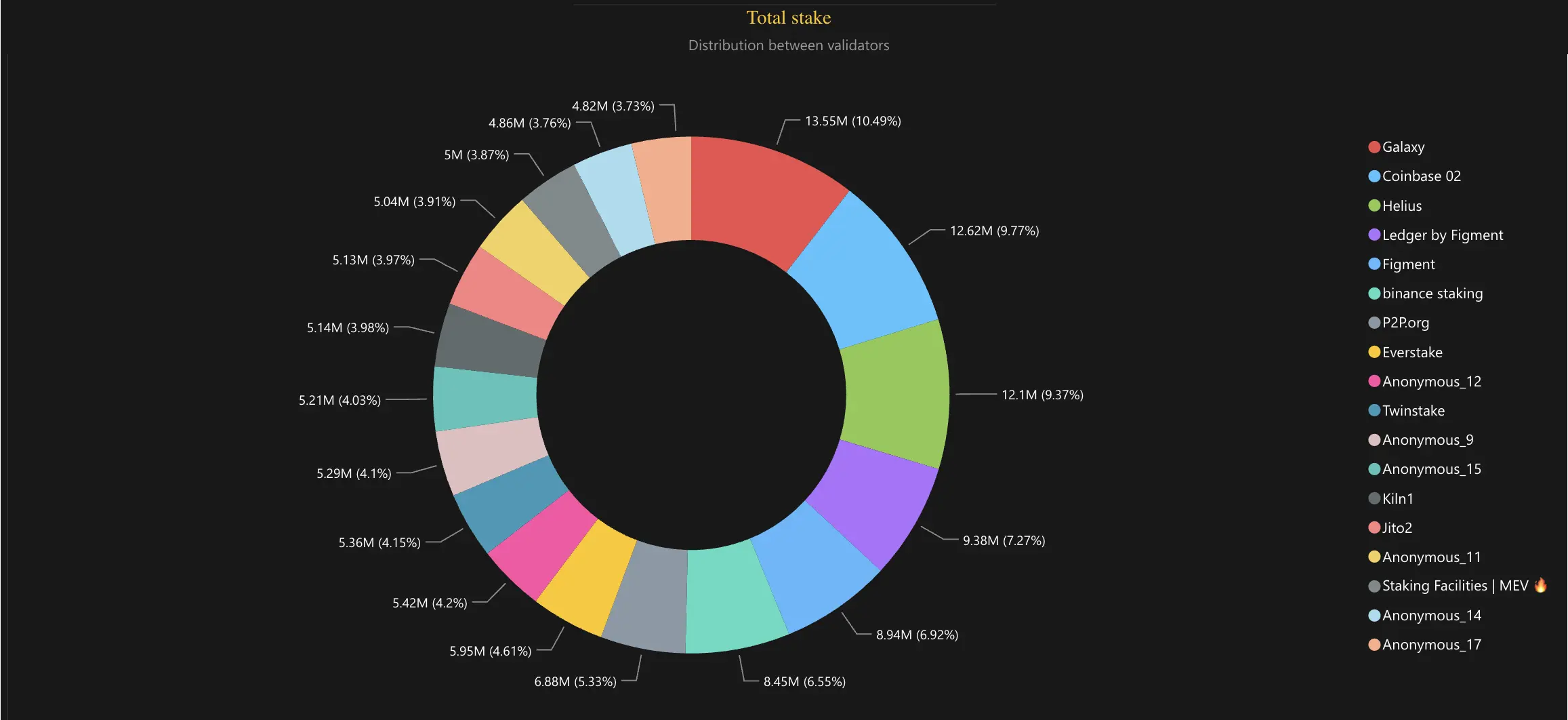
Staking Accounts Distribution
Everstake (highlighted in yellow on the chart) stands out as the leading validator by the number of delegators, with over 166,000 stake accounts. Start staking your SOL with Everstake, your trusted staking provider.
Ledger by Figment takes second place with more than 101,000 stake accounts. Helius comes third with 16,000 stake accounts. The chart below illustrates the distribution in superminority.
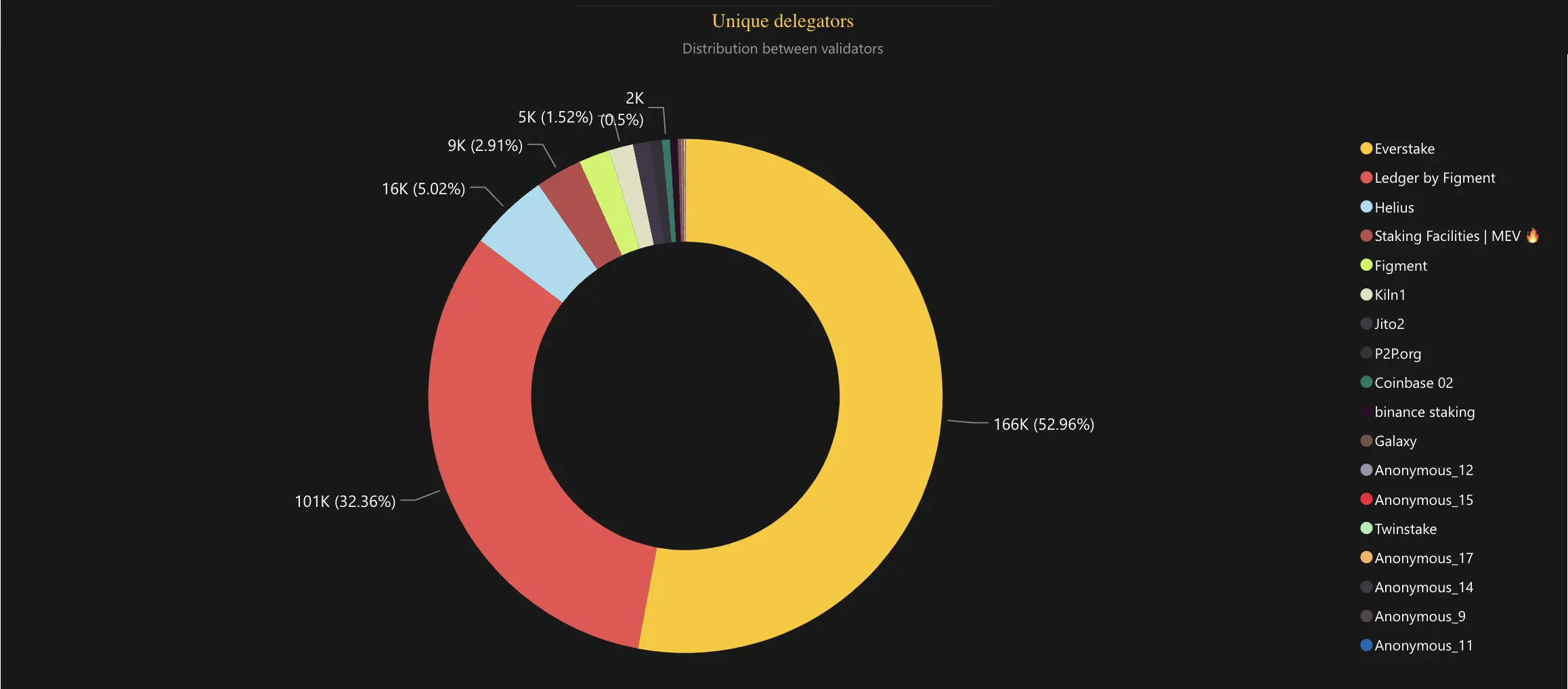
Delegator Behavior Analysis (Total Stake and APY)
From January to July 2024, the total stake and staking yield in Solana experienced a noticeable decline. Yet, starting in September 2024, there was an observable recovery for both metrics. This rebound suggests renewed confidence and participation among delegators. Factors contributing to this recovery likely include more attractive staking incentives and more favorable market conditions. The graph below provides a detailed depiction of trends in total stake and APY over the year.
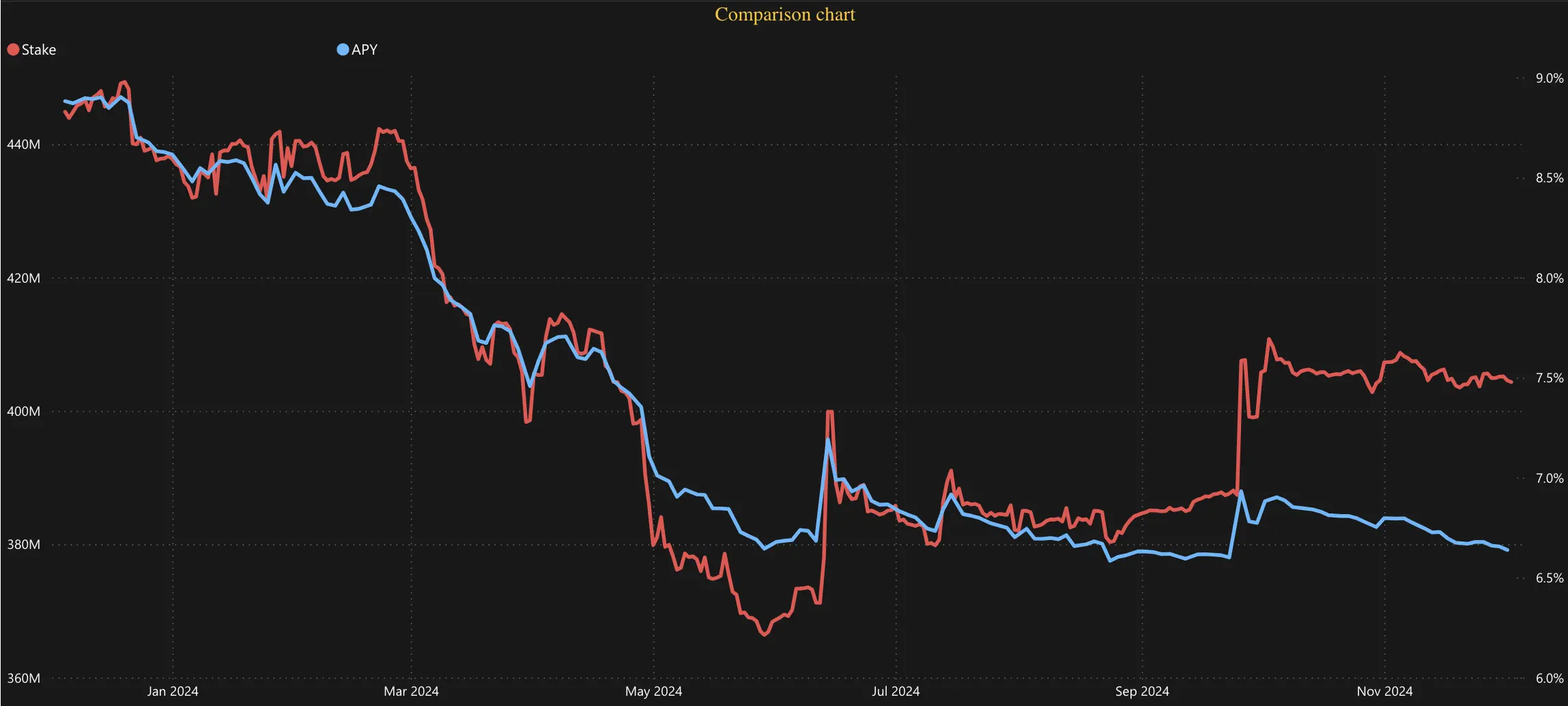
Solana Network Performance
Performance is a cornerstone of the Solana ecosystem, enabling it to scale effectively while accommodating a growing number of applications and users. Solana's architecture is optimized for high throughput, low latency, and minimal transaction costs.
Solana has maintained exceptional reliability for almost a year, operating with 100% uptime and no incidents. The most recent occurred on February 6, 2024, at 09:53 UTC, when the Solana Mainnet Beta experienced a disruption that halted block finalization. Engineers across the ecosystem promptly collaborated to identify and address the root cause. Simultaneously, validator operators worked together to coordinate a cluster restart. By 14:55 UTC, consensus was restored, concluding the incident after approximately five hours.
Additional details on this event are available in the full incident report here.
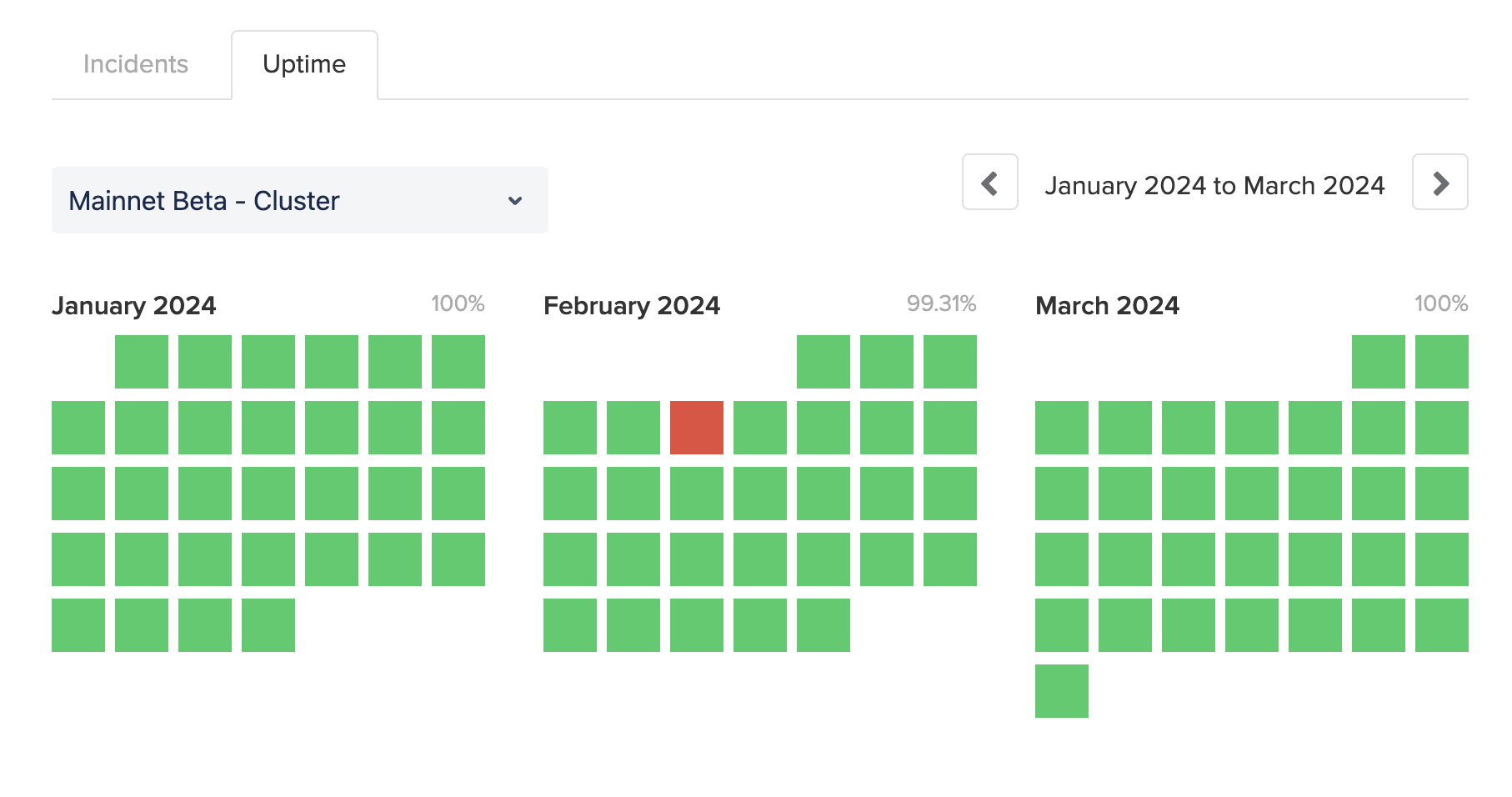
Source: status.solana.com
Since then, the Solana network has operated without incidents, consistently achieving 100% uptime.
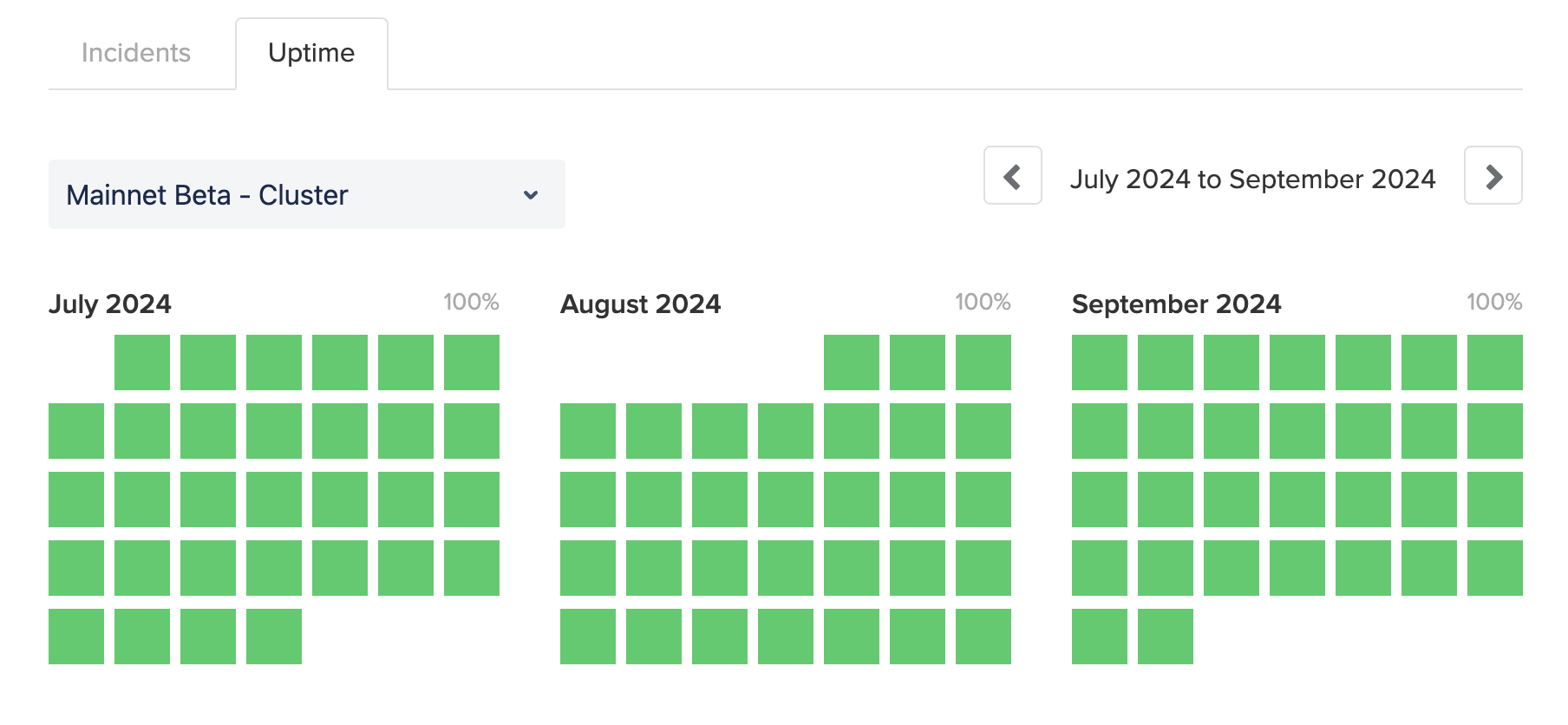
Source: status.solana.com
Solana Restaking
Solana restaking is an important innovation offering the dual benefit of maximizing staking benefits while reinforcing network security. Token holders reallocate their staked SOL beyond traditional staking, which enables participation in dApps and validator operations. Restaking enhances capital efficiency and supports the broader ecosystem through increased utility. It also contributes to Solana’s scalability and operational efficiency.
The key contributors to the SOL restaking ecosystem in 2024 are as follows.
-
Jito offers a flexible and efficient solution for networks to achieve consensus and economic security across various on-chain and off-chain activities. Serving as both a staking and restaking product, Jito (Re)staking enhances token utility, strengthens security mechanisms, provides an insurance fund, scales base layers, and creates risk backstops. It is applicable to a wide range of pre-existing networks, particularly those with automated yet centralized processes.
-
Solayer is a restaking protocol built natively on the Solana blockchain, designed to optimize network bandwidth for on-chain dApps while reinforcing Layer 1 security. By enabling users to restake their staked assets, Solayer enhances the security of multiple networks simultaneously, leveraging existing tokens to provide additional security layers without necessitating extra capital investment.
-
Picasso enables Solana holders to contribute their staked tokens to secure a wide range of dApps, networks, and infrastructure across the ecosystem. Picasso Restaking offers an opportunity for community members to actively participate in the growth of the Solana ecosystem while earning additional benefits for their contributions.
Future Prospects
The Solana ecosystem has already garnered significant attention from both venture capitalists and large institutions, and ongoing strategic partnerships and investments will likely continue to drive adoption and increase the network's credibility.
At the same time, an increasing number of DeFi protocols, NFTs, gaming projects, and infrastructure tools are being built on the platform. The developer community enjoys hackathons, grants, and a developer-friendly environment, which creates a creative atmosphere within the professional community that greatly contributes to the ecosystem’s further evolution. In the coming year, simplified programming environments are expected to attract even more developers. A strong and engaged global community will undoubtedly be among the key factors in the network's future success.
Both technologically and socially, the Solana community is well-positioned to maintain its competitive edge in the coming year. The network's advantages, coupled with its passionate and expanding user base, offer a solid foundation for continued success.
Disclaimer
Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates is a software platform that provides infrastructure tools and resources for users but does not offer investment advice or investment opportunities, manage funds, facilitate collective investment schemes, provide financial services or take custody of, or otherwise hold or manage, customer assets. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates does not conduct any independent diligence on or substantive review of any blockchain asset, digital currency, cryptocurrency or associated funds. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates’s provision of technology services allowing a user to stake digital assets is not an endorsement or a recommendation of any digital assets by it. Users are fully and solely responsible for evaluating whether to stake digital assets.
Sign Up for
Our Newsletter
By submitting this form, you are acknowledging that you have read and agree to our Privacy Notice, which details how we collect and use your information.