
ETH
Ethereum
crypto
staking
ETHEREUM (ETH) STAKING INSIGHTS & PROTOCOL ANALYSIS: FIRST HALF OF 2025 | EVERSTAKE
Explore the Ethereum staking report for the first half of 2025. Key metrics, validator performance, the Ethereum ecosystem trends and staking.
JUL 30, 2025
Table of Contents
Key insights & takeaways
Methodology
The Pectra upgrade: Ethereum’s defining moment of H1 2025
In-depth: key Pectra’s EIPs
Network activity & user engagement
Ethereum staking landscape
Ethereum Foundation: leadership, governance & treasury
Security events
Future prospects
Conclusion
Share with your network
Key insights & takeaways
-
Pectra upgrade activated May 7, 2025, bringing faster blobs, flexible staking, and smart-contract powers to regular wallets.
-
Over 31.5 million new unique addresses were created in H1 2025, nearly matching the total address growth in all of 2024.
-
Daily active users (DAU) grew steadily from ~380K to ~420K.
-
Staked ETH reached an all-time high of 35.3 million ETH, representing over 29% of the supply.
-
Liquid restaking grew fast, from 6.3% to 7.6% of staked ETH, with over 550,000 ETH inflows.
-
Validator entry queue hit record highs, peaking at 450,000 ETH.
-
The Ethereum Foundation split its leadership into strategic and operational branches, introduced structured governance practices, and began publishing detailed reports on how it allocates capital and manages its treasury.
-
Ethereum Foundation deployed $32M in grants and 50K ETH in DeFi support to strengthen the ecosystem.
-
ETH staking ETFs are awaiting SEC approval, which may unlock regulated yield exposure.
Methodology
We pulled data from on-chain analytics platforms (beaconcha.in, Etherscan, Token Terminal), Ethereum Foundation publications, validator dashboards, and transparency reports. Where possible, we cross-referenced multiple data sources to ensure accuracy and contextual depth. This report reflects developments between January and June 2025 and focuses on staking trends, protocol upgrades, ecosystem dynamics, and governance shifts.
The Pectra upgrade: Ethereum’s defining moment of H1 2025
The first half of 2025 was defined by the Pectra upgradeEthereum’s biggest since Shanghai. Activated on May 7, it introduced 11 Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) focused on usability, staking mechanics, security, and scalability.
Development timeline
-
November 2023: Work on Pectra begins
-
January 2025: 11 EIPs approved
-
March 2025: Final testing on Sepolia, Holesky, Hoodi
-
May 7, 2025: Mainnet activation
Guiding principles
Pectra was built around three guiding principles: addressing real user needs, enhancing scalability and throughput, and improving validator flexibility. As Ethereum’s validator landscape grew more complex and demanding, with increasing interest from institutions and complex restaking frameworks, the need for more robust validator mechanics became clear.
Pectra responded by raising validator balance caps, improving withdrawal operations, and easing queue pressure.
EIP categories
-
User experience: EIP-7702
-
Staking upgrades: EIP-7251, 7002, 6110
-
Data scaling: EIP-7691, 7840, 2537
In-depth: key Pectra’s EIPs
While Pectra included 11 EIPs, we focus here on three that stand out for their transformational impact across scaling, staking, and user experience. These upgrades address long-standing technical bottlenecks and lay the foundation for Ethereum’s next growth phase.
EIP-7691: DOUBLING BLOB THROUGHPUT
This upgrade increases the amount of data each block can carry by doubling the average number of “blobs,” off-chain data chunks used by Layer-2 rollups, from 3 to 6, with a new maximum of 9 per block. By expanding the bandwidth for rollups, Ethereum takes a meaningful step toward lower L2 fees and greater throughput without changing base-layer mechanics.
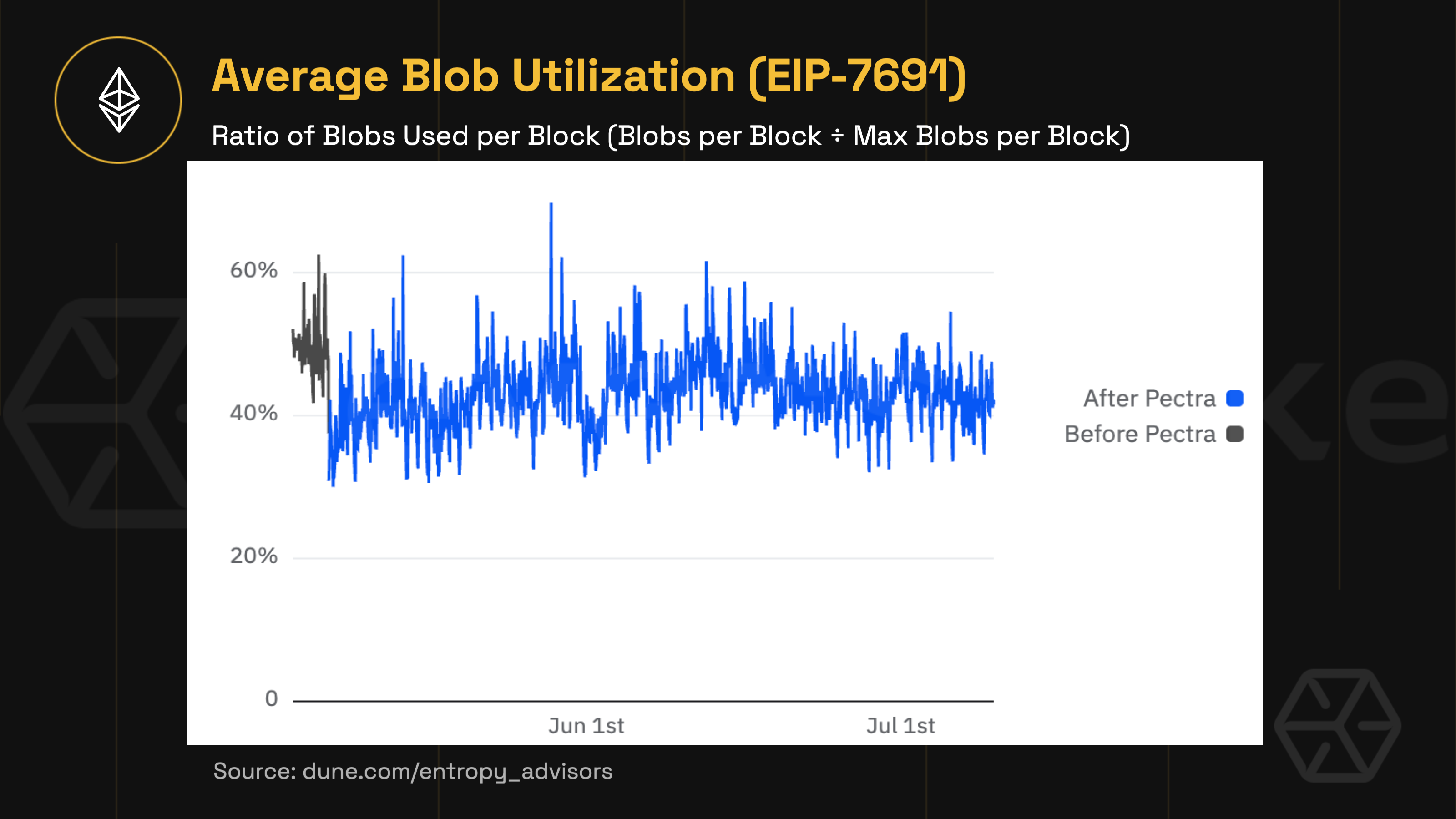
-
Average blob usage sits at ~40–45%, indicating available headroom for rollup scaling without any observed impact on security or performance.
-
Unused blob capacity poses no risk: it simply lays the groundwork for future network expansion as rollup adoption accelerates.
-
Sets the stage for Ethereum to support higher-volume rollup activity in the coming upgrades.
EIP-7251: COMPOUNDING VALIDATOR
EIP-7251 lifts the validator effective balance cap from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH, allowing large operators to consolidate stakes and run fewer, more efficient nodes. It also enables automatic compounding of staking rewards and reduces slashing penalties by 128x, from 1/32 to just 1/4096 of the validator’s balance.
-
Over 750,000 ETH is now held by validators using this model.
-
Only ~3,700 validators have adopted it so far, as many await long-term performance data.
-
Reduces operational overhead and enhances capital efficiency for high-balance validators.
-
The softened slashing curve offers better protection against temporary failures or downtime.
EIP-7702: SMART CONTRACT CAPABILITIES FOR EOAS
This proposal enhances externally owned accounts (EOAs) with smart contract functionality, enabling batched transactions, gas payments in non-ETH tokens, and delegated execution rights without requiring users to migrate to a contract wallet. It’s a major usability upgrade that blurs the line between EOAs and smart contracts.
-
Since the Pectra activation, EOA-to-contract delegations have exceeded 700,000, marking a significant shift in how accounts interact on Ethereum, both in terms of flexibility and responsibility
-
But there is another side of the coin: roughly 65–70% of known EIP-7702 delegations have been linked to phishing or scam activity
Security recommendations:
-
Delegate rights only through official websites and trusted plugins; avoid suspicious links and always verify contract addresses before signing
-
If you have any doubts, review the contract source code and avoid interacting with closed-source contracts; take your time before approving transactions
-
Work is ongoing to improve safety; some leading wallets (for example, MetaMask) have already added built-in risk warnings for EIP-7702
Network activity & user engagement
Ethereum’s on-chain activity saw steady growth in H1 2025.
Unique addresses
31.5 million new unique addresses were created in the first half of 2025—almost as many as during the entire year of 2023 (35.38M) or 2024 (40.48M). The strongest growth occurred in March and April:
-
March: +6.7M new addresses (~217K/day)
-
April: +5.7M new addresses (~192K/day)
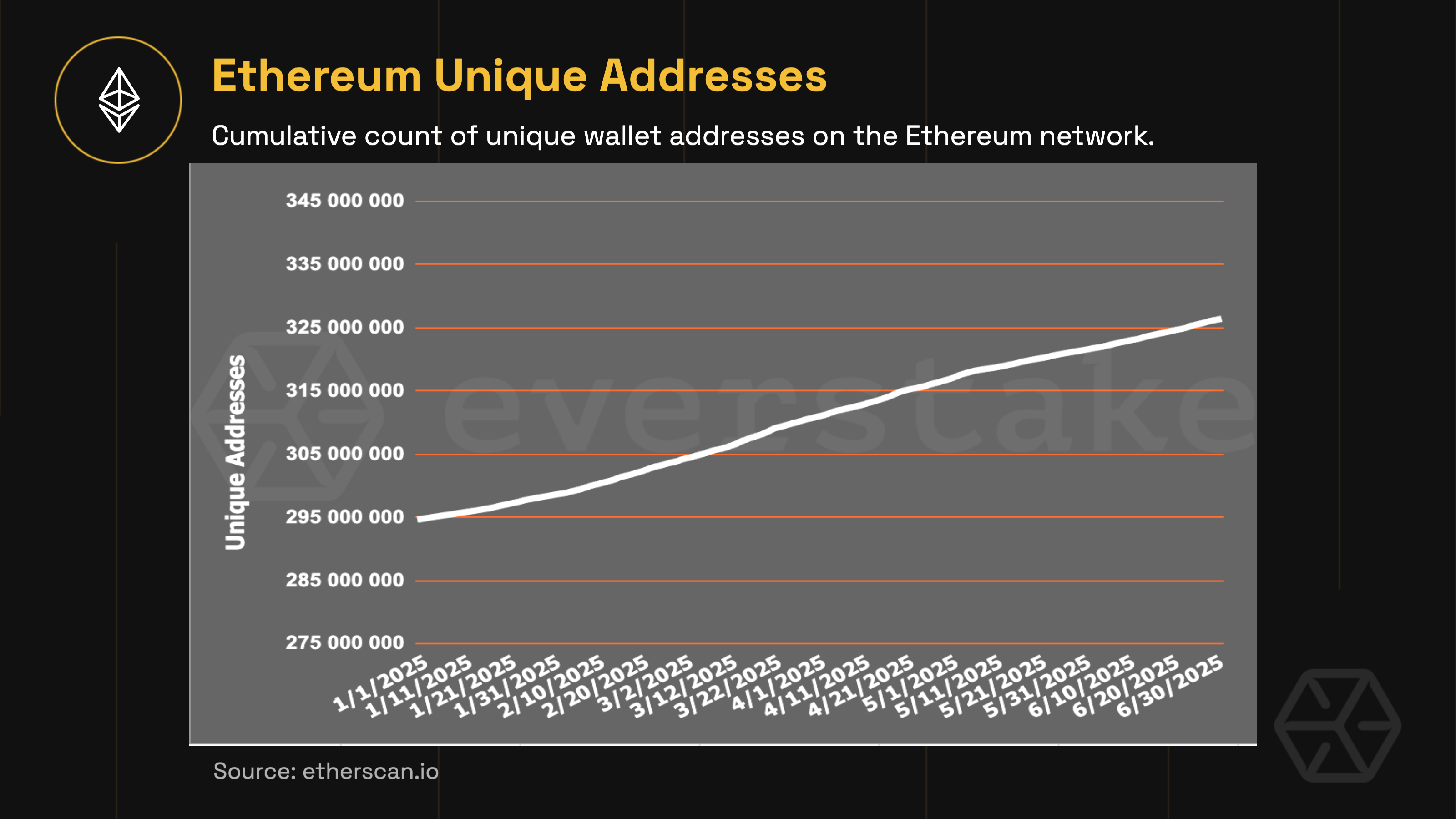
This spike was fueled by growing anticipation for the Pectra upgrade. Throughout March, Ethereum’s core testnets: Holesky, Sepolia, and Hoodi—completed integration testing of key EIPs. Then, in early April, developers officially confirmed May 7, 2025 as the Pectra mainnet activation date, further amplifying on-chain activity and user engagement.
Daily transactions
Ethereum processed an average of 1,278,709 transactions per day in H1 2025, with daily activity ranging between 1.1 million and 1.5 million. This represents a 9.3% increase, or about +113,000 daily transactions—compared to 2024. For reference, daily transaction volume grew by 11.83% between 2023 and 2024, or approximately +123,000 daily transactions
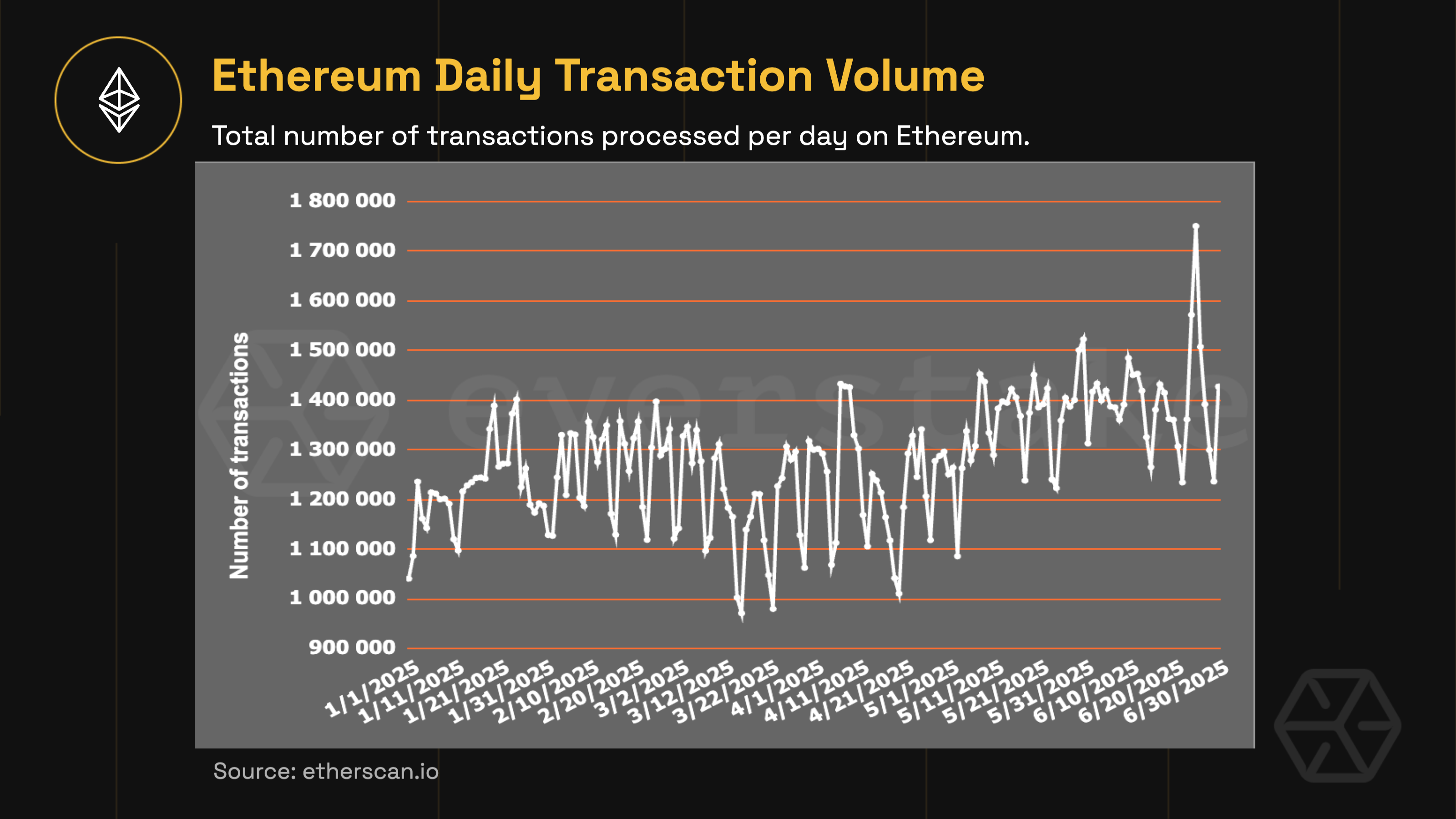
This steady increase in transaction volume reflects real, consistent usage—not just short-term spikes. Ethereum continues to attract active users across DeFi, NFTs, and Layer-2s, showing that its infrastructure isn’t just scaling technically but being adopted at scale.
Daily active users (DAU)
Ethereum has shifted from a period of volatility and rapid growth (2017–2022) into a more stable maturity phase. In 2023–2024, DAU hovered between 300K and 450K. In H1 2025, that baseline solidified: daily active users consistently ranged from 380K to 420K.
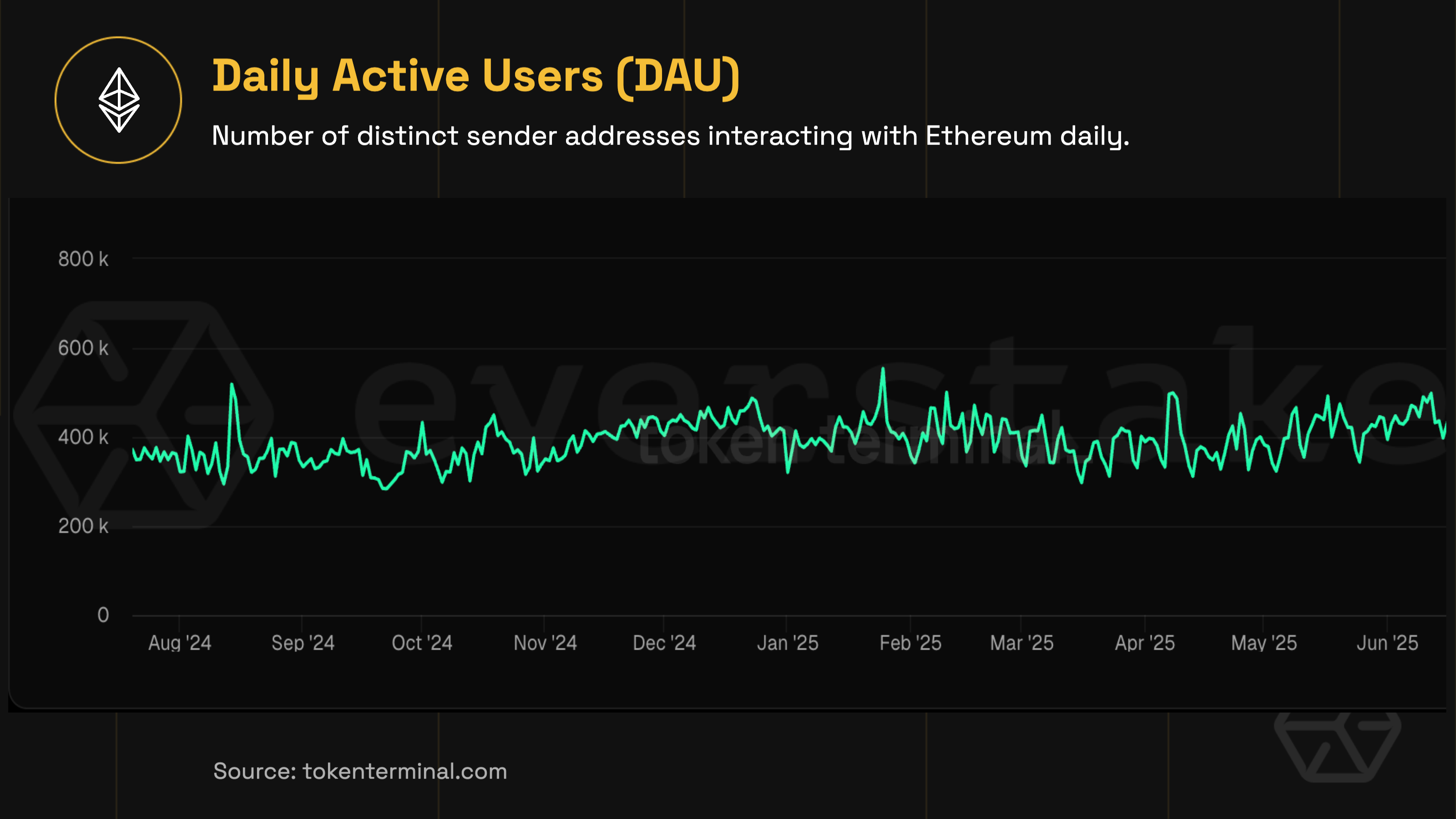
The Pectra activation on May 7 acted as a catalyst, prompting protocol updates and increased blob-related activity. Sustained DAU strength was also driven by continued DeFi adoption, scaling via major Layer-2s, institutional staking participation, and Ethereum’s growing role as reliable infrastructure rather than a speculative asset.
Ethereum staking landscape
Ethereum’s staking ecosystem continued to mature in the first half of 2025. Total ETH staked grew from 34 million in January to 35.3 million by the end of June, pushing the staking ratio to a record 29% of the total supply. Until mid-to-late May, total ETH staked had remained flat at around 33.5–34 million. The most notable surge occurred in late May, shortly after the Pectra upgrade went live.
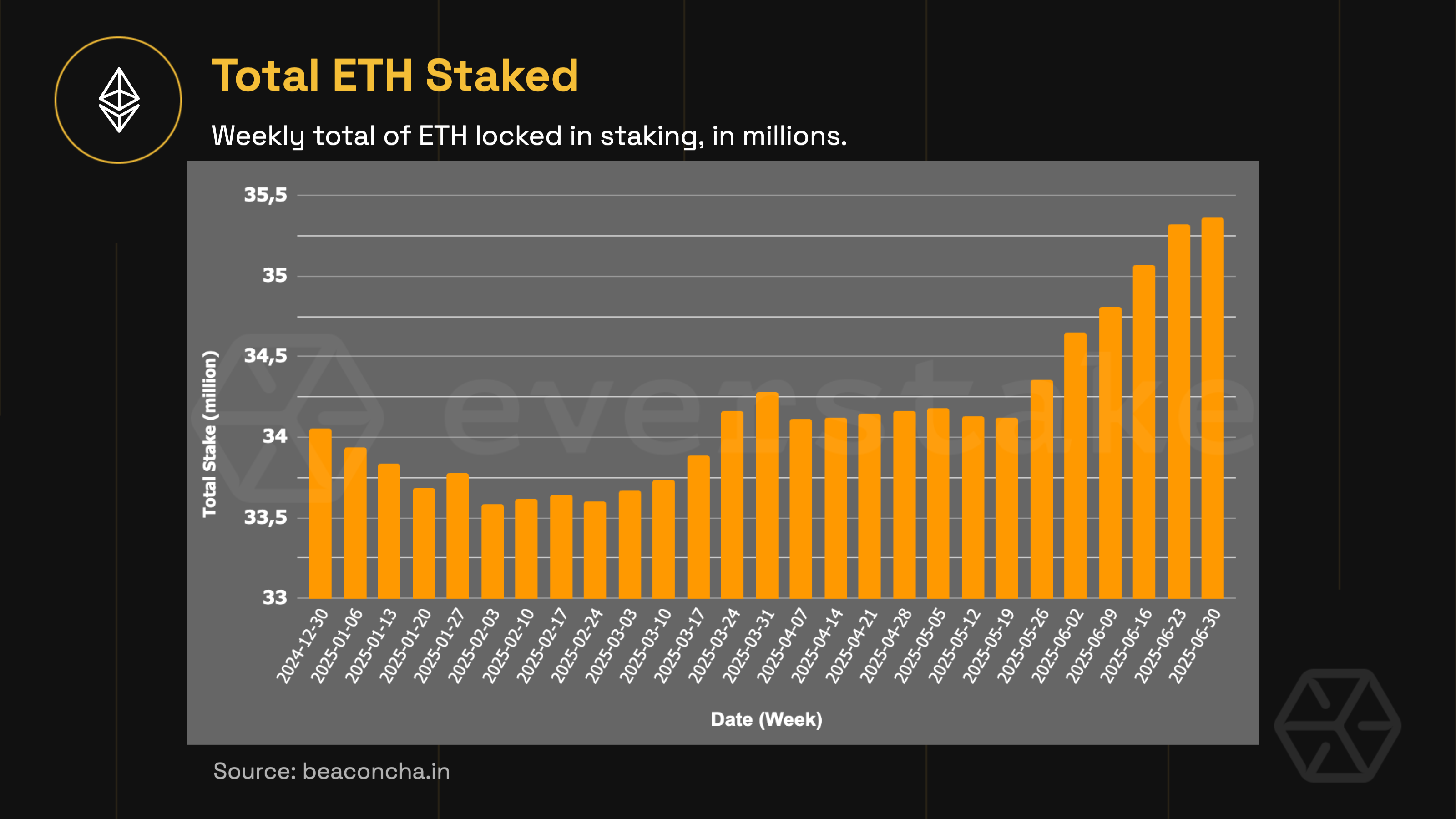
A key factor behind the surge was the introduction of EIP‑7251, which increased the validator cap from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH. Large holders used this to combine stakes and spin up high-balance validators. As of June, these “0x02” validators controlled more than 750,000 ETH—over 2% of the total staked ETH.
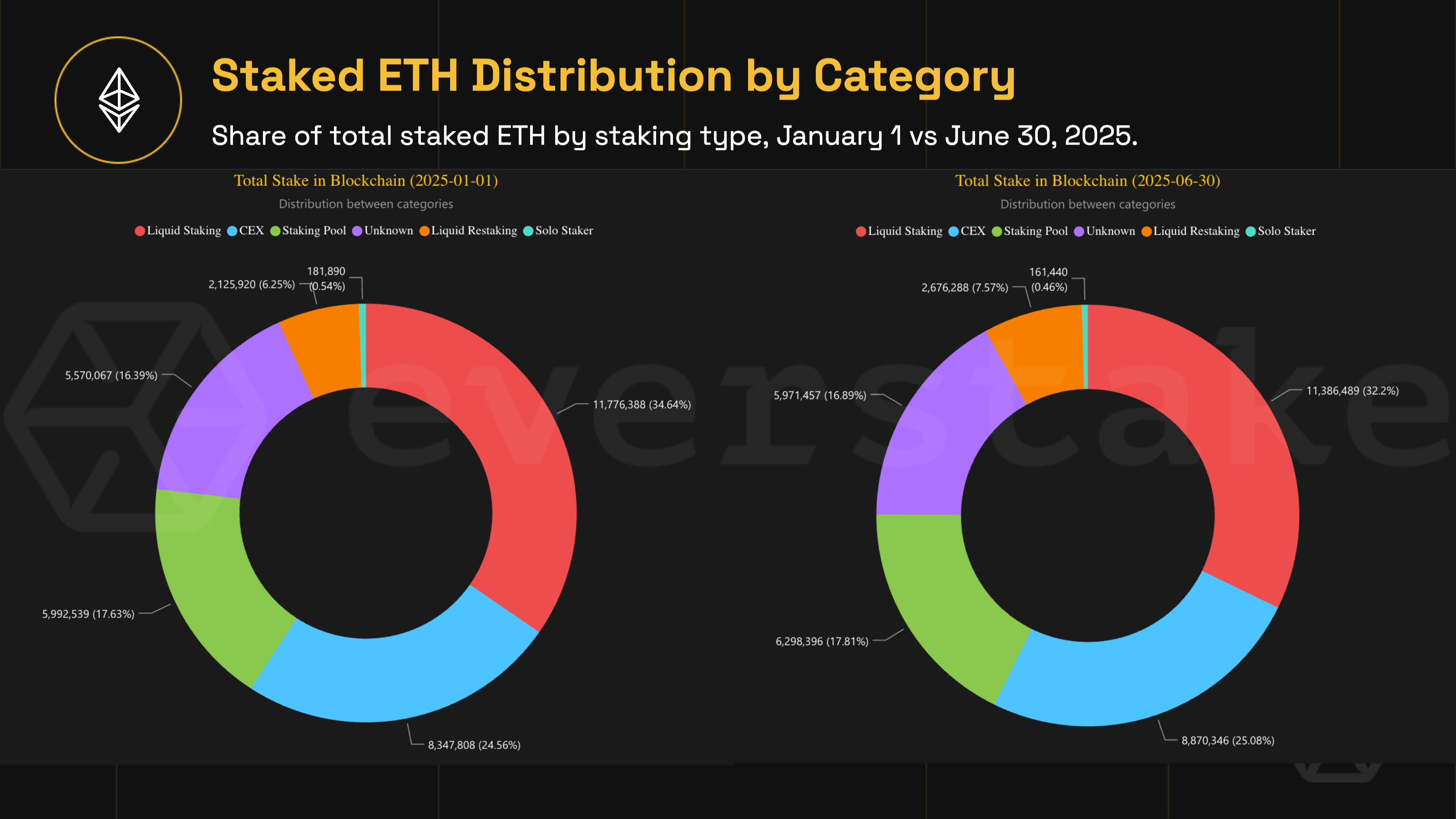
The composition of staked ETH also shifted during this period.
-
Liquid staking saw a moderate decline, dropping from 34.6% to 32.2% (a net decrease of 390,000 ETH).
-
On the other hand, centralized exchange platforms gained ground—their share rose by 0.5%, absorbing around 520,000 ETH in new deposits.
-
Staking pools posted a modest rise, climbing from 17.6% to 17.8%, while liquid restaking emerged as the biggest mover.
-
This rapidly growing segment expanded from 6.3% to 7.6%, bringing in over 550,000 ETH.
We noted that restaking protocols like EigenLayer are driving these flows, offering "double" returns on the same ETH stake. This is highly attractive to institutional investors and sophisticated users alike.
Demand for validator participation also reached record highs. In late May, the validator entry queue swelled to 450,000 ETH, with an average wait time ranging from 4 to 7 days. This bottleneck was driven largely by a wave of institutional participants, spurred by the promise of ETH staking ETFs and opportunities for layered yield strategies such as those enabled by restaking protocols.
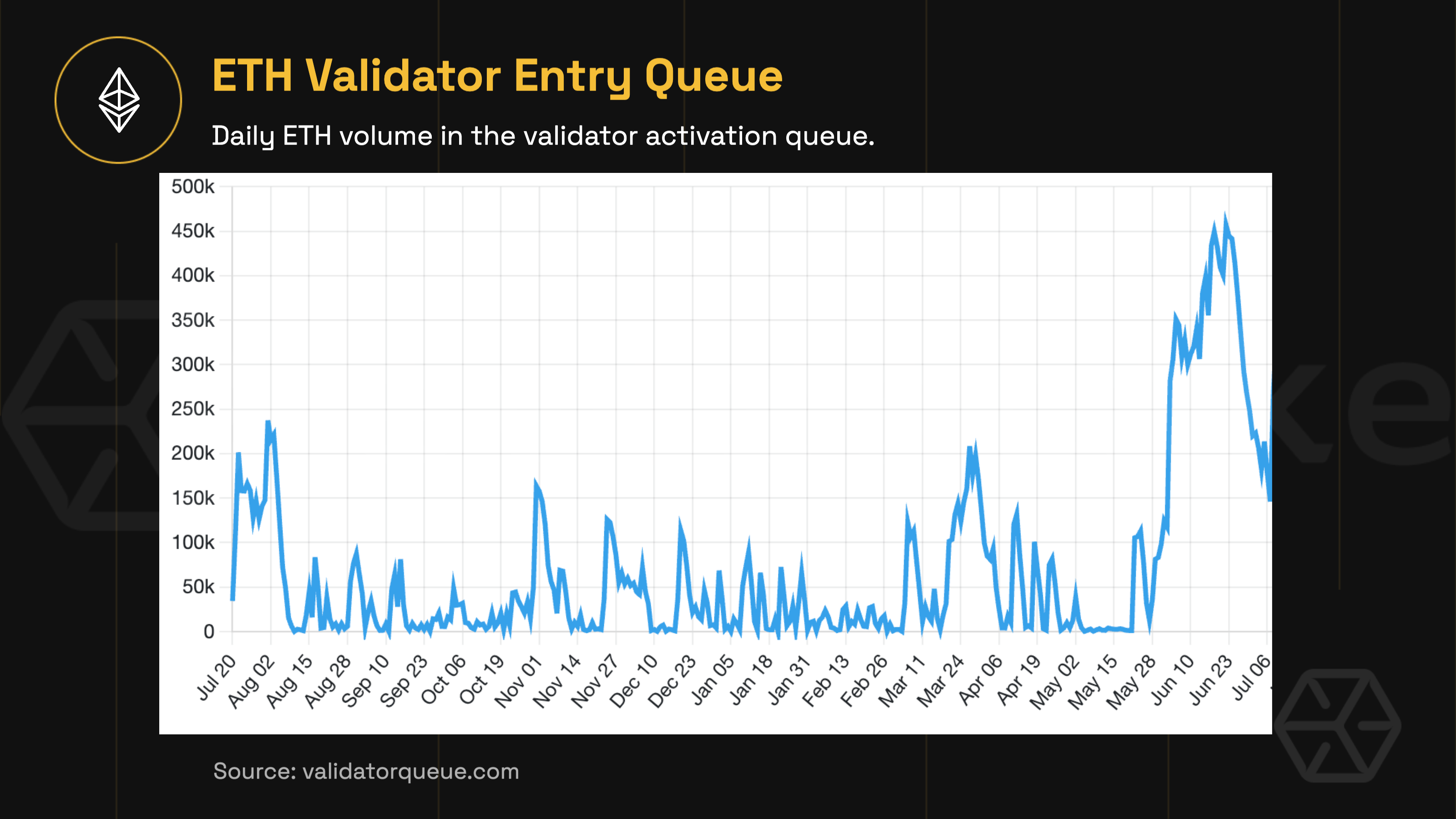
Why the shift? For one, institutions increasingly sought ways to optimize returns through restaking frameworks and complex DeFi integrations. Meanwhile, the simplicity and convenience of CEX staking continued to appeal to less technical participants. And finally, a new class of sophisticated stakers began leveraging cross-protocol routes to maximize both control and yield, further diversifying Ethereum’s validator landscape.
As a result, the Ethereum staking space is no longer just about receiving additional rewards but developing into an ecosystem of layered strategies and institutional-grade infrastructure.
Ethereum Foundation: leadership, governance & treasury
Against the backdrop of Ethereum’s technical upgrades, the Ethereum Foundation (EF) underwent its own pivotal transformation in the first half of 2025—one centered on transparency, leadership structure, and capital deployment.
The EF allocates grants and manages a sizable treasury and plays an active role in protocol development. It regularly participates in ACDC, ACDE, and ACDT calls, where its research team advocates for new EIPs to be integrated into the protocol.
The Foundation launched a dedicated X account in January 2025 to bridge a long-standing communication gap with the community. It also began publishing quarterly transparency reports that detail grant allocations, treasury activity, and protocol-related expenditures—marking a new chapter of public accountability.
On the governance front, the EF formalized a distributed leadership model with a clear division between strategic and operational roles:
-
January 18, 2025: Vitalik Buterin announced the restructuring via X.
-
Late February - Early March: Aya Miyaguchi transitioned from Executive Director to President, focusing on strategic vision and external partnerships.
-
March 1, 2025: Hsiao-Wei Wang and Tomasz Stańczak were appointed as Co-Executive Directors, leading technical direction and operations, respectively.
-
February 2025: Danny Ryan joined the “Etherealize” initiative as a Co-Founder and exited the core EF team.
Following these structural changes, the Foundation significantly increased its ecosystem support:
-
In Q1 2025, the EF distributed $32 million in grants—almost triple the $8-13 million range per quarter in 2024.
-
It also deployed 50,000 ETH (≈$165 million at the time) into protocols like Aave, Safe, and others to earn yield and strengthen DeFi infrastructure.
-
According to Arkham data, approximately 200,000–220,000 ETH sits in the Foundation’s known multisigs. EF’s own reports cite total ETH holdings near 300,000, suggesting that around 23% of its on-chain treasury and roughly 16% of its total reserves are currently deployed in DeFi.
-
These actions were formalized in the EF Treasury Policy, published on June 4, 2025, which established clear rules for asset allocation across liquid funds, staking operations, and DeFi investments. The policy emphasizes transparency, risk management, and sustainable yield generation.
However, the first half of 2025 was not without setbacks. On February 21, the Ethereum ecosystem experienced its largest recorded exploit to date, when hackers, later attributed to North Korean–linked groups, stole 401,000 ETH (~$1.5 billion) from Bybit by exploiting a vulnerability in the platform’s cold-to-warm wallet transfer system. In the aftermath, ETH fell 8% from around $2,845 to $2,600, with market sentiment remaining bearish into April, when the price reached lows near $1,400.
Security events
While Ethereum’s core protocol remained stable in H1 2025, the broader ecosystem saw several notable security incidents. These events highlight the ongoing challenges of operating in a permissionless, composable environment where the attack surface grows alongside innovation.
Bybit exploit
-
Feb 21: 401,000 ETH stolen (~$1.5B)
-
Attributed to North Korea-linked actors
-
ETH dropped from $2,845 → $2,600; hit ~$1,400 in April
EIP-7702 scams
-
65–70% of delegations abused in phishing campaigns
-
Wallet teams responded with extra verification layers
Future prospects
Ethereum’s development roadmap remains ambitious. With Pectra complete, attention now turns to the next major upgrade, Fusaka, and long-term research proposals like RISC-V. Meanwhile, institutional interest intensifies, with large players positioning themselves ahead of staking ETF approvals and new infrastructure shifts, especially around the anticipated launch of ETH staking ETFs.
These future catalysts reflect Ethereum’s dual ambition: to scale aggressively while remaining open, programmable, and decentralized.
Fusaka upgrade (target: Q4 2025–Q1 2026)
Slated for late 2025 or early 2026, Fusaka is Ethereum’s next big step toward long-term scalability. Building on the groundwork laid by Pectra, this upgrade bundles 12 EIPs currently under testnet evaluation, though that number may change depending on how testing progresses: one EIP was already dropped as of late July. The focal point is data availability and execution efficiency, with PeerDAS leading the charge.
-
PeerDAS (EIP-7594): A decentralized data availability sampling system, PeerDAS enables nodes to verify blobs by sampling rather than downloading in full—which drastically reduces costs for L2s.
-
Blob Expansion: The target number of blobs per block will grow from 6 to 48, and the maximum from 9 to 72. This exponential leap aims to supercharge rollup throughput while maintaining cost efficiency.
-
Additional Improvements: Fusaka also includes gas usage optimizations, refined code execution limits, and proposer scheduling upgrades—all of which contribute to a leaner, more scalable protocol.
Fusaka was originally expected to include EOF (EVM Object Format), a proposal to restructure how contract bytecode is stored and executed. While it promised improved auditability and optimization potential, it was dropped due to technical uncertainties and community pushback. EOF is now being reprioritized for the following upgrade, Glamsterdam.
RISC-V proposal
Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin floated a radical idea in early 2025: replacing the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) with an RISC-V-based execution layer. RISC-V, an open standard instruction set architecture, could dramatically accelerate smart contract processing. Preliminary testing suggests potential performance gains between 2x and 100x, depending on use case and implementation.
But such a shift wouldn’t come without trade-offs. Moving to RISC-V would raise serious backward compatibility concerns and could fragment the developer community. Tooling and infrastructure would need significant rework, and consensus around such a fundamental change would likely take years.
For now, RISC-V remains a long-term research direction, not a scheduled fork. Instead of rushing into another EVM tweak, the Ethereum team is focused on stabilizing Fusaka’s core features and deferring EOF to Glamsterdam.
ETH staking ETFs
On the institutional side, anticipation grows around the SEC’s approval of Ethereum staking ETFs. These instruments are expected to provide regulated, yield-bearing exposure to ETH for a wide range of investors—a milestone that could redefine how traditional finance engages with staking.
Under the proposed structure, custodians like Coinbase, BitGo, and Gemini would manage ETH on behalf of fund participants. Staking rewards would either be reflected in the fund’s NAV or distributed as dividends. Early projections estimate net yields between 1.7% and 2.2%.
However, Ethereum imposes an unstaking period of at least 9-10 days, which can stretch to 20-30 or even 50 days when network activity spikes. To remain liquid and meet redemptions, ETFs cannot stake their entire balance at once and must hold a portion of ETH unbonded. This reduces the effective staking yield, typically around 3%, to about 50-70% of that figure. After deducting custodian and operator fees, net yields are expected to settle between 1.7% and 2.2%. For comparison, Canada’s 3iQ Ether ETF delivers an APR of about 1.6–1.7%.
Major players such as BlackRock, Grayscale, and Franklin Templeton have already filed ETF applications, signaling a strong institutional appetite for Ethereum’s staking economy.
Conclusion
The first half of 2025 marked a turning point. Ethereum proved it could evolve its architecture without missing a beat. Pectra raised validator limits, doubled blob capacity, and extended smart contract capabilities to EOAs without compromising protocol stability.
Meanwhile, Ethereum's staking economy transformed. Restaking frameworks gained serious traction. Validator queues surged. ETF approval moved from speculation to expectation.
The Ethereum Foundation, too, shifted gears: publishing transparency reports, deploying capital strategically, and formalizing governance roles.
Ethereum is no longer preparing for institutional engagement but operates within it. The focus has shifted from building credibility to executing at scale.
Ethereum isn’t just holding ground. It’s making that ground more valuable, block by block.
Disclaimer
Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates is a software platform that provides infrastructure tools and resources for users but does not offer investment advice or investment opportunities, manage funds, facilitate collective investment schemes, provide financial services or take custody of, or otherwise hold or manage, customer assets. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates does not conduct any independent diligence on or substantive review of any blockchain asset, digital currency, cryptocurrency or associated funds. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates’s provision of technology services allowing a user to stake digital assets is not an endorsement or a recommendation of any digital assets by it. Users are fully and solely responsible for evaluating whether to stake digital assets.
Sign Up for
Our Newsletter
By submitting this form, you are acknowledging that you have read and agree to our Privacy Notice, which details how we collect and use your information.