
The ABCs of Crypto
Common Staking Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Staking looks simple, but the wrong validator, missed compounding, or poor security can quietly cut your rewards. Here’s how to avoid the mistakes many delegators still make.
NOV 21, 2025
Table of Contents
1. Choosing the Wrong Validator
2. Ignoring Staking Parameters and Network Rules
3. Misconfiguring a Node or Validator Setup
4. Overlooking Reward Compounding
5. Ignoring Security Best Practices
6. Failing to Monitor Validator Performance
7. Misjudging Liquidity and Lock-Up Risks
8. Overestimating Rewards and Underestimating Risks
9. Forgetting Tax Implications
10. Neglecting Governance Participation
Conclusion
Share with your network
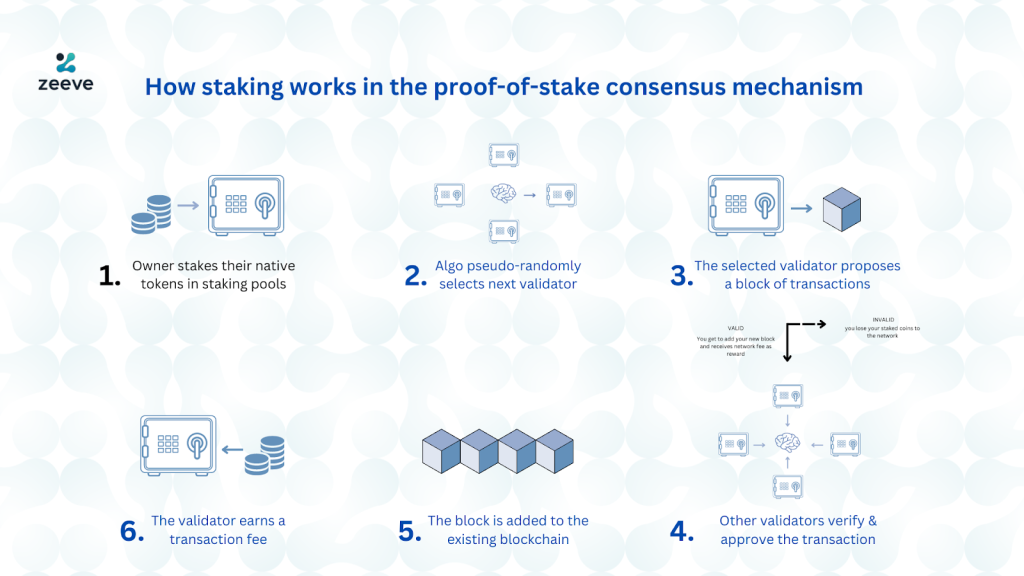
Crypto staking is one of the most popular methods for receiving rewards from a blockchain in decentralized finance. That said, despite its growing popularity, staking remains an area where many participants lose potential rewards or, even worse, their own funds due to avoidable staking mistakes.
Understanding these staking errors and staking risks is crucial for both newcomers and experienced users. This article explores the most frequent pitfalls in staking, their causes, and practical methods of avoiding them.
1. Choosing the Wrong Validator
Selecting a validator is one of the most critical decisions in the staking process. Yet, many users delegate their tokens to validators without proper research.
A poor validator choice can lead to several staking risks.
- Downtime and missed rewards: Validators that are frequently offline may not participate in block validation, leading to lower or missed rewards.
- Slashing penalties: If a validator acts maliciously or fails to follow protocol rules, delegators can lose a portion of their staked assets in a process known as slashing.
- Poor communication or transparency: Some validators fail to share performance data or updates, leaving delegators uninformed about potential issues.
Reliable vs. Unreliable Validator comparison
Let’s take a look at a tentative comparison between a reliable and unreliable validator.
| Criteria | Reliable Validator | Unreliable Validator |
| Uptime | 99.9%+ | Frequent downtime |
| Commission | Transparent, fair rate (5–10%) | Unclear, suspiciously high or low, or constantly changing |
| Slashing Record | None or minimal | History of slashing |
| Communication | Active community channels | Inactive or opaque |
| Security | Audited infrastructure | Unknown or unverified setup |
How to avoid this mistake
Before staking, review validator uptime, commission rates, community reputation, and security audits. The easiest way to do this is to check the validator’s profile on the official explorer for uptime history, missed blocks, slashing records, and any unusual commission changes. You can also visit the validator’s website to verify published audits or certifications, and explore community channels for feedback from other delegators.
Finally, consider spreading your stake across more than one reputable validator. A broader distribution helps reduce dependency on a single operator and lowers potential exposure to staking risks like downtime or slashing.
For a detailed breakdown of what validator uptime really means and how to evaluate it, you can refer to our complete guide on uptime analysis.
2. Ignoring Staking Parameters and Network Rules
Each blockchain has unique staking mechanics, including lock-up periods, unbonding times, minimum staking amounts, and reward structures. Failing to understand these parameters is one of the most overlooked staking mistakes.
For example, on some networks, unbonding your tokens can take several days or even weeks, while it can be a matter of minutes in others. Either way, during this time, your assets won’t generate rewards and cannot be used in transactions. In other cases, failing to meet the minimum staking threshold could result in your tokens sitting idle.
How to avoid this mistake
- Read the staking documentation for your chosen network
- Understand the reward cycle, lock-up periods, and compounding options
- Consider whether you need liquidity before having your tokens locked up, especially if there’s a program that requires them to remain staked for a specified period
Being informed about network-specific parameters prevents staking misconfiguration, a technical error that can result in missed opportunities or frozen assets.
3. Misconfiguring a Node or Validator Setup
Some users prefer to run their own validator nodes to receive a higher share of rewards. While this can be more lucrative, it also brings about new staking risks and operational challenges.
The aforementioned staking misconfiguration, such as using outdated software, weak security settings, or improper network connections, can result in missed blocks, performance penalties, or even slashing events.
If you’re considering running a validator yourself, practical case studies can help clarify performance requirements. Our Agave–Cherry Servers guide breaks down real-world node optimization techniques.
Common Misconfigurations
- Failing to update the node software on time
- Using unsecured private keys or keeping them online (or in a location accessible to other people)
- Not setting up monitoring tools to detect downtime
- Underestimating hardware requirements
How to avoid this mistake
If you run a validator, follow best DeS Ops practices: automate monitoring, maintain redundancy, and use hardware with sufficient performance margins. For most users, delegating to a trusted professional validator is safer and eliminates much of this operational complexity, as well as the significant costs associated with running your own infrastructure.
For Solana specifically, we also have a step-by-step guide on choosing and setting up a node using Cherry Servers infrastructure, which illustrates the core configuration principles in practice.
4. Overlooking Reward Compounding
One of the biggest staking errors users make is failing to reuse their rewards. Staking rewards can be claimed periodically, but if you don’t restake them, you miss out on compound growth.
This can significantly reduce long-term rewards. For example, an annual reward rate of 10% can effectively grow closer to 10.5–11% if compounded monthly. Over multiple years, this difference becomes substantial.
How to avoid this mistake
- Regularly claim and restake your rewards if the network allows it
- Use staking dashboards or automated tools to track and optimize compounding schedules
- Be aware of transaction fees, since, on some networks, frequent claiming may not be cost-effective
Avoiding missed rewards staking is about maintaining discipline and consistency. Automation can help, but users should still periodically verify their reward activity.
5. Ignoring Security Best Practices
Security remains one of the most underestimated aspects of staking. Even when tokens are locked in smart contracts or delegated to validators, poor security hygiene can still lead to irreversible losses.
Common security-related staking mistakes most usually include falling prey to phishing attacks, having your private key exposed, or using a compromised device.
How to avoid this mistake
- Use hardware wallets for staking whenever possible
- Verify validator and staking platform URLs carefully
- Keep software and firmware updated
- Never share your private key or seed phrase, and keep them in a safe place that only you can access
- Do not trust unsolicited emails or messages with lucrative promises
Maintaining good cybersecurity hygiene reduces exposure to staking risks that are unrelated to network performance but equally damaging.
6. Failing to Monitor Validator Performance
Delegating once and forgetting about it is another widespread staking error. Validators’ performance can change over time due to technical issues, governance decisions, or changes in operator behavior.
Failing to monitor your validator can result in lower rewards, unexpected downtime, or even slashing if the validator begins to misbehave.
How to avoid this mistake
- Utilize on-chain dashboards and analytics platforms to monitor validator uptime and assess reward performance
- Set alerts for downtime or missed blocks
- Re-delegate to a different validator if performance drops consistently
Ongoing monitoring helps maintain reward consistency and mitigates the risk of missed rewards staking due to validator negligence.
7. Misjudging Liquidity and Lock-Up Risks
Many staking programs require locking tokens for a specific duration. During this lock-up period, your tokens cannot be moved or sold. This creates a liquidity trade-off that some users underestimate.
If market conditions change (for instance, if the token price drops sharply), your assets may become illiquid, forcing you to absorb losses. Conversely, if prices rise, you might miss selling opportunities.
How to avoid this mistake
- Stake only the portion of tokens you can afford to lock for the full duration
- Consider liquid staking solutions, which issue derivative tokens representing staked assets
- Diversify between liquid and traditional staking to maintain flexibility
Being mindful of liquidity prevents financial stress and supports a sustainable staking strategy.
8. Overestimating Rewards and Underestimating Risks
Some platforms advertise extremely high annual percentage yields (APY) to attract delegators. That said, these numbers often fluctuate or come with hidden staking risks such as token inflation, liquidity constraints, or complex reward mechanisms.
A high APY doesn’t always translate into better opportunities, especially if token prices decline or inflation erodes value. Moreover, a high promised rewards rate should trigger a more thorough research of such a platform.
| Factor | High-APY Token | Moderate-APY Token |
| Advertised APY | 100% | 15% |
| Token Inflation | 80% | 5% |
| Net Real Yield | 20% | 10% |
| Liquidity | Low | High |
How to avoid this mistake
Always consider real rewards, which account for inflation and token price movement. Research whether reward rates are sustainable, and avoid staking with projects that promise unrealistic returns without transparent economics.
9. Forgetting Tax Implications
In many jurisdictions, staking rewards are considered taxable income. Ignoring this reality is a non-technical but financially significant staking mistake.
Failure to track and report rewards correctly can result in unexpected tax liabilities or penalties. The exact rules vary by country, but generally, users must record both the time of reward receipt and the fair market value at that moment.
How to avoid this mistake
- Use crypto tax software to log staking transactions automatically
- Keep a record of reward distributions and claim events
- Consult a tax professional familiar with digital asset taxation
Good tax hygiene complements operational discipline and helps maintain compliance.
10. Neglecting Governance Participation
Many Proof-of-Stake networks also grant voting rights to token holders. Delegators who ignore governance proposals may miss the opportunity to influence network upgrades, reward policies, or validator regulations.
While this doesn’t cause immediate staking errors, it can indirectly impact rewards and network stability over time.
How to avoid this mistake
- Follow governance updates for the network you stake on.
- Participate in key votes that affect reward distribution or validator criteria
- Consider delegating to validators with a proven track record of transparent governance
Being engaged helps ensure that your staking strategy aligns with the network’s long-term vision.
Conclusion
Staking can be a reliable source of receiving incentives from a blockchain, but it requires knowledge and discipline. The most common staking mistakes stem from inattention, a lack of research, or technical missteps, such as staking misconfiguration and security oversights. So, always be sure to do proper research before engaging in staking activities.
***
All metrics displayed on the website, including without limitations value of staked assets, total number of active users, rewards rates, and networks supported, are historical figures and may not represent the actual real-time data.
Share with your network
Related Articles

The ABCs of Crypto
Crypto Validators Explained in Depth: The Core of Proof-of-Stake Networks
Validators are the core operators of Proof-of-Stake blockchains. This guide explains how they work, how they differ from delegators, and why they are critical to network security.
DEC 05, 2025

The ABCs of Crypto
Institutional vs Retail Staking: Key Differences
A clear breakdown of how institutions and individual users approach staking, and why their risks, requirements, and responsibilities differ.
DEC 01, 2025

The ABCs of Crypto
Institutional Staking Risks and How to Manage Them
From slashing to custody failures, institutional staking demands more than simple delegation. This guide breaks down the risks and the controls that matter.
NOV 25, 2025
Disclaimer
Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates is a software platform that provides infrastructure tools and resources for users but does not offer investment advice or investment opportunities, manage funds, facilitate collective investment schemes, provide financial services or take custody of, or otherwise hold or manage, customer assets. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates does not conduct any independent diligence on or substantive review of any blockchain asset, digital currency, cryptocurrency or associated funds. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates’s provision of technology services allowing a user to stake digital assets is not an endorsement or a recommendation of any digital assets by it. Users are fully and solely responsible for evaluating whether to stake digital assets.
Sign Up for
Our Newsletter
By submitting this form, you are acknowledging that you have read and agree to our Privacy Notice, which details how we collect and use your information.