TL;DR
A delegator is someone who participates in crypto staking without requiring any technical setup.
Instead of operating a validator node, they delegate their tokens to a trusted validator who helps run the blockchain.
- Your tokens stay in your wallet; they’re just locked for staking;
- The validator uses that stake to help validate blocks and keep the network secure;
- You automatically receive a share of the staking rewards in return.
In short: you don’t give away your crypto; you let it work for the network while it stays yours.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains rely on participants, known as validators, to verify transactions and secure the network. However, since running a validator requires technical setup and constant uptime, most users participate through staking delegation—assigning their tokens to a trusted validator who performs the work on their behalf.
In this article, we’ll explain what a delegator in staking is, how staking delegation works, and how it differs from running a validator.
What Is a Delegator in Crypto Staking?
In crypto staking, a delegator is a token holder who participates in a Proof-of-Stake network by assigning their stake to a validator instead of running their own node. This process, known as staking delegation, enables users to support the network’s operation, receive rewards, and participate in governance without managing any technical infrastructure.
In simple terms, a delegator trusts a validator to act on their behalf. The validator utilizes the combined stake of multiple delegators to propose and validate new blocks, with rewards distributed proportionally among all participants. Notably, the delegator’s tokens remain in their own wallet; they are not transferred to the validator. Instead, the delegator temporarily grants the validator the right to use their stake as voting power within the consensus mechanism.
By delegating, users help maintain network decentralization and security, ensuring that no single validator gains excessive control over the network. This model makes staking accessible to everyone, not just technically skilled node operators, and forms the backbone of most modern PoS ecosystems.
How Staking Delegation Works
Although details vary by blockchain, the general staking delegation process follows the same logic:
- Choosing a validator
The delegator starts by selecting a validator, usually based on reputation, uptime, commission rate, and performance metrics. This choice is crucial, as rewards and potential risks (such as slashing) depend on the validator’s reliability.
- Delegating tokens
The delegator uses a compatible wallet or staking interface to delegate tokens. During this step, the tokens remain in the delegator’s wallet; they are not transferred to the validator, but are temporarily locked to signal participation in consensus.
- Getting rewards
Once the validator successfully proposes or verifies blocks, the network distributes staking rewards. These are shared proportionally among all delegators, minus the validator’s commission fee.
- Redelegating or undelegating
Delegators can redelegate (switch validators) or undelegate (withdraw tokens) at any time. However, undelegation usually triggers an unbonding period, which can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the network. During this time, the tokens cannot get rewards or be transferred.
This staking delegation meaning locking tokens to strengthen the network and share in rewards, lies at the core of Proof-of-Stake systems. It provides a balance between accessibility and decentralization, enabling both technical and non-technical users to contribute to blockchain security.
What Are Staking Pools?
A staking pool combines many users’ stakes into one collective delegation. This increases the validator’s weight and provides more stable, predictable rewards, especially for smaller holders.
Here’s how it works:
- Delegation: Users add their coins to the pool, effectively delegating their stake without transferring ownership.
- The staking pool: All contributions are combined into one large stake, which gives the pool higher weight in the validator selection process.
- Validator selection: The blockchain randomly selects a pool (or its associated validator) to validate the next block.
- Block validation and rewards: The pool confirms transactions and secures the chain. When the block is validated, the network issues rewards.
- Fee deduction and reward sharing: The pool operator takes a small commission fee, and the remaining rewards are distributed among all delegators proportionally.
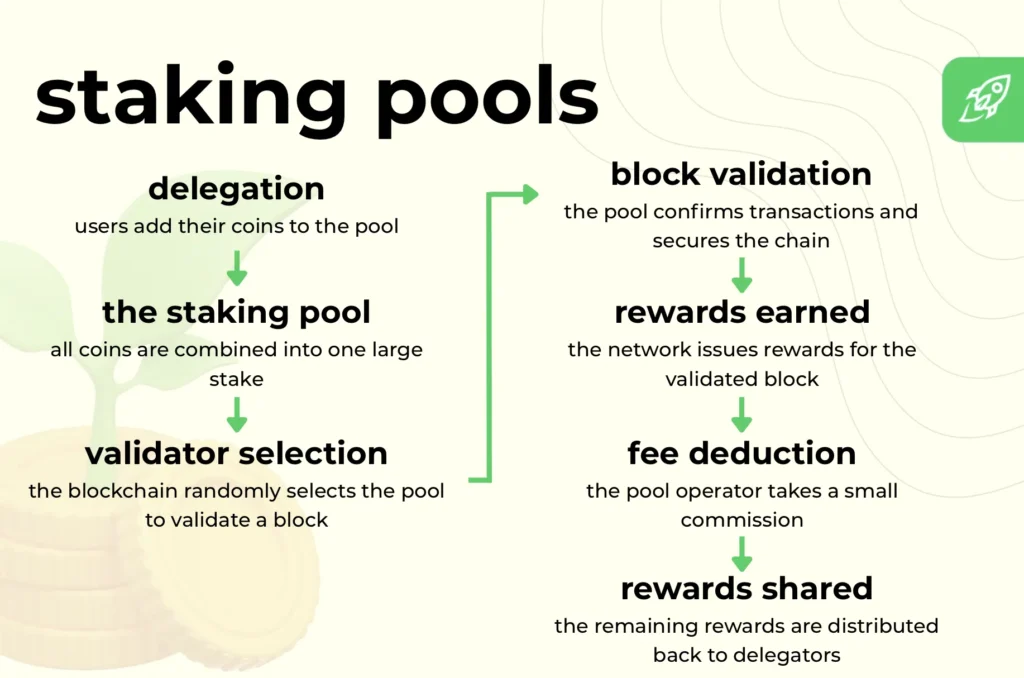
In essence, staking pools simplify participation for users who don’t want to run validators or stake large amounts on their own. They make staking delegation more inclusive and efficient, allowing anyone to contribute to network security while getting steady rewards.
What’s the Difference between Delegator and Validator?
In Proof-of-Stake networks, both validators and delegators play essential roles in maintaining blockchain security and decentralization.
However, their responsibilities and levels of involvement differ significantly. Understanding the distinction between the two helps users decide how they want to participate in staking. Both sides are equally vital: validators secure the network through continuous operation, while delegators contribute capital that amplifies the validator’s influence and helps maintain the network’s decentralization.
| Role | Validator | Delegator |
| Main function | Runs a node to validate transactions and produce new blocks | Delegates tokens to a validator to support the network indirectly |
| Technical skills required | High: requires hardware setup, uptime maintenance, and software management | Low: staking can be done easily through a wallet or platform |
| Rewards | Receives staking rewards and may charge a commission from delegators | Gets a share of staking rewards minus validator’s commission |
| Risks | Can be penalized for downtime or misbehavior (slashing) | Faces indirect risks if the chosen validator is slashed |
| Control over tokens | Tokens are self-owned and directly staked | Tokens remain in the delegator’s wallet but are locked during staking |
In the context of delegator vs validator, the key takeaway is participation choice, whether to manage infrastructure as a validator or take a more accessible, low-maintenance route as a delegator. Both together ensure that Proof-of-Stake ecosystems remain secure, fair, and sustainable.
Benefits and Risks of Being a Delegator
Becoming a delegator is one of the most accessible ways to participate in a blockchain network and get staking rewards. However, like any blockchain activity, delegation comes with both advantages and potential drawbacks. Understanding both sides helps users make informed decisions.
Benefits
- No technical setup required: Delegators don’t need to run or maintain validator nodes; staking can be done through simple wallet interfaces or staking dashboards.
- Passive participation: By delegating, users help secure the network and contribute to decentralization without constant monitoring.
- Staking rewards: Delegators receive a portion of the validator’s rewards, distributed proportionally to their delegated stake.
- Flexible engagement: Many networks allow redelegation, meaning users can easily switch validators if performance or commission rates change.
Risks
- Validator performance: If the chosen validator experiences downtime or behaves maliciously, delegators’ rewards may decrease or, in extreme cases, be partially slashed.
- Lock and unbonding periods: Delegated tokens are locked for a certain duration. During unbonding, they can’t be transferred or traded.
- Changing network conditions: Protocol updates, commission adjustments, or governance decisions can influence staking outcomes.
Ultimately, being a delegator strikes a balance between convenience and responsibility. It’s a low-barrier entry point into staking, but it still requires research and vigilance, especially when selecting a trustworthy validator.
How to Choose a Reliable Validator
Selecting the proper validator is the most crucial decision a delegator makes—it directly impacts rewards, network security, and the safety of delegated tokens. Here’s what to consider when choosing a reliable validator for staking delegation:
1. Reputation and track record
Look for validators with a proven history of uptime, transparency, and consistent participation in network governance. Many blockchains offer public dashboards that allow you to view validator statistics, including performance, the number of delegators, and voting activity.
2. Commission rate
Validators charge a small commission fee (typically between 2% and 10%), which is deducted from staking rewards. A lower rate doesn’t always mean better value; reliability and technical performance matter more in the long run.
3. Security and transparency
Trusted validators pay attention to robust infrastructure, security audits, and compliance certifications (like SOC 2 or ISO/IEC 27001). These measures demonstrate professional operation and a commitment to protecting delegators’ assets.
4. Communication and community presence
Active validators often share updates, publish performance reports, and communicate openly with their community, a good sign of reliability and accountability.
Many users prefer trusted operators such as Everstake, known for running thousands of nodes across multiple networks with enterprise-level reliability and transparent operations. A well-chosen validator ensures consistent rewards, minimizes slashing risks, and enhances the overall network’s stability.
Delegation in 2025: What’s New
The staking landscape continues to mature, but delegation remains at its core.
In 2025, token holders aren’t just looking for rewards; they care about reliability, transparency, and security when choosing validators. New technologies, such as modular consensus layers and cross-protocol coordination tools, make delegation more flexible, allowing users to support multiple networks through the same trusted operators.
Even with these innovations, the foundation stays unchanged: trusted validators, non-custodial participation, and informed delegators who value decentralization over speculation.
Stake with Everstake | Follow us on X | Connect with us on Discord
***
Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates is a software platform that provides infrastructure tools and resources for users but does not offer investment advice or investment opportunities, manage funds, facilitate collective investment schemes, provide financial services or take custody of, or otherwise hold or manage, customer assets. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates does not conduct any independent diligence on or substantive review of any blockchain asset, digital currency, cryptocurrency or associated funds. Everstake, Inc. or any of its affiliates’s provision of technology services allowing a user to stake digital assets is not an endorsement or a recommendation of any digital assets by it. Users are fully and solely responsible for evaluating whether to stake digital assets.
